Overview
The article examines the pivotal role of Optical Character Recognition (OCR) in optimizing efficiency within land records management by automating the digitization and extraction of information from diverse document formats. It underscores that the implementation of OCR significantly diminishes processing time and errors, as demonstrated by case studies that reveal marked improvements in both speed and accuracy. Consequently, OCR emerges as an indispensable tool for title researchers striving to modernize their workflows.
Introduction
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) represents a transformative technology, fundamentally altering the management of land records by converting static documents into dynamic, searchable data. As the necessity for efficient information retrieval escalates, it becomes imperative for title researchers and legal professionals to comprehend the significant impact of OCR on operational workflows.
Despite its notable advantages—such as improved accuracy and decreased processing times—challenges remain, including handwriting recognition and document quality issues.
How can organizations effectively navigate these hurdles to fully leverage the capabilities of OCR in land records management?
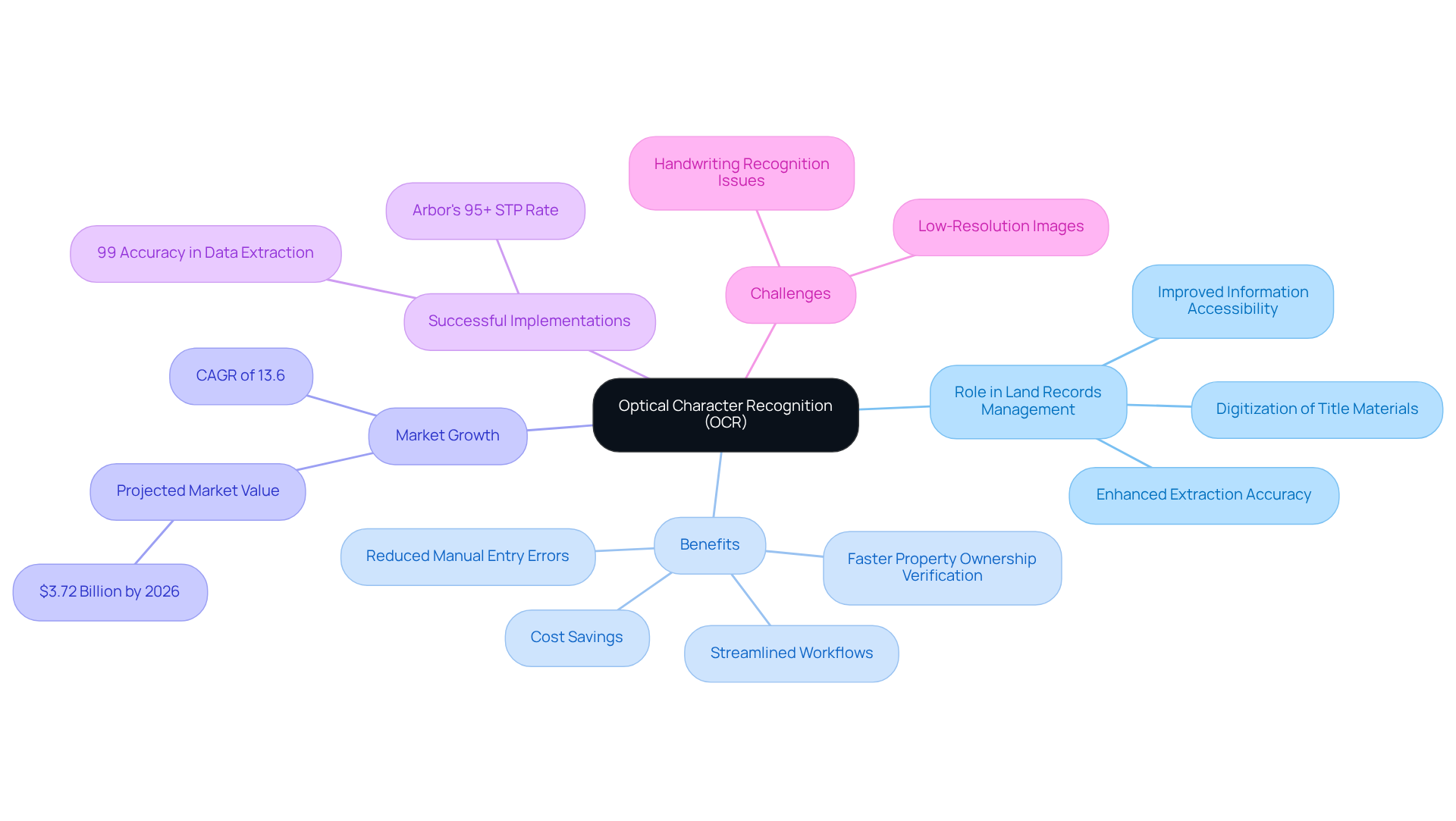
Define Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and Its Role in Land Records Management
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) represents a transformative technology that converts various file types—such as scanned documents, PDFs, and images captured by digital cameras—into editable and searchable content. In the realm of land records management, using OCR for land records plays a vital role in digitizing extensive collections of title materials, which significantly improves both information accessibility and extraction accuracy.
By employing advanced machine learning algorithms, contemporary OCR systems proficiently recognize and interpret intricate legal language and a variety of document formats, rendering them essential tools for title researchers. Furthermore, using OCR for land records management systems not only streamlines workflows but also reduces manual entry errors, resulting in faster and more reliable property ownership verification.
With the to reach $3.72 billion by 2026, boasting a compound annual growth rate of 13.6%, this growth underscores the critical role of OCR in enhancing operational efficiency within the real estate sector. Successful implementations of OCR have demonstrated its capacity to automate information extraction processes up to ten times faster than manual methods, thereby reducing labor costs and improving compliance with regulatory standards.
For instance, Arbor achieved a straight-through processing rate exceeding 95% and over 99% accuracy in data extraction following the adoption of OCR techniques, showcasing its practical effectiveness. Industry leaders emphasize that using OCR for land records is essential for modernizing title research methodologies, ensuring that legal professionals can adeptly manage and retrieve crucial information from vast archives.
However, it is essential to recognize potential challenges, such as issues with handwriting recognition and low-resolution images, which can impact OCR performance.
Explore the Benefits of OCR for Title Research and Document Processing
The implementation of systems using OCR for land records in title research and file processing presents significant advantages that markedly enhance operational efficiency. Primarily, by using OCR for land records, the time necessary to manage extensive file collections is reduced through automated information extraction, allowing title researchers to concentrate on analysis rather than manual input.
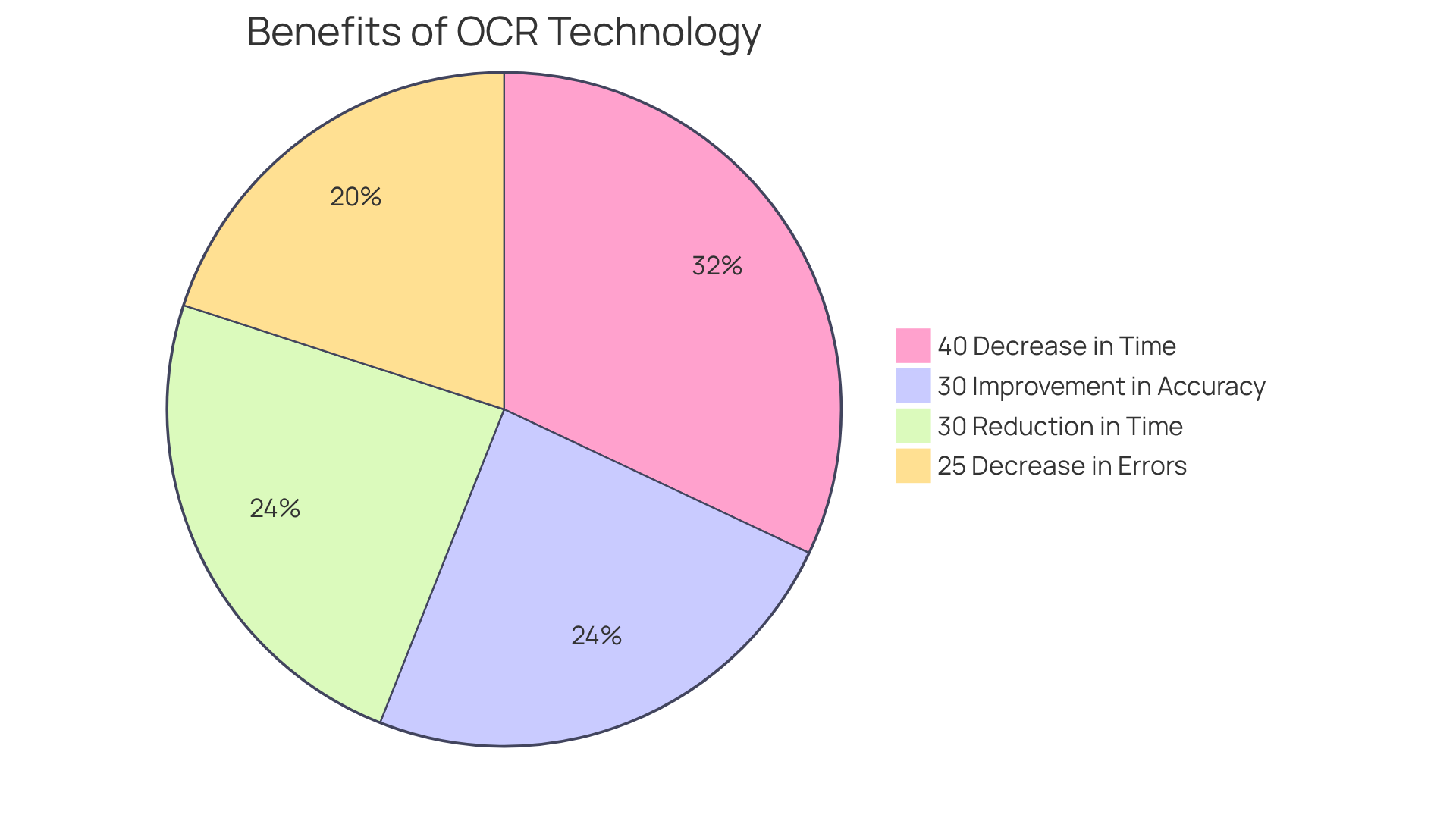
For instance, a title research company that adopted OCR methods experienced an impressive 40% decrease in processing time and a 30% improvement in accuracy for their title abstracts. This enhancement is critical in legal contexts where .
Furthermore, OCR enhances information management by streamlining the searching and classification of files, which is vital for compliance with legal standards and maintaining audit trails. As noted by Aaron Bianchi, "OCR technology identifies and retrieves text and information from files with high precision, minimizing the requirement for manual information entry."
The incorporation of OCR not only optimizes workflows but also results in substantial cost savings, with financial institutions reporting a 30% reduction in processing time and a 25% decrease in data entry errors. Consequently, this establishes the importance of using OCR for land records as an indispensable tool in contemporary land records management, capable of scaling to accommodate varying volumes of files.
Implementing OCR: Best Practices for Title Researchers
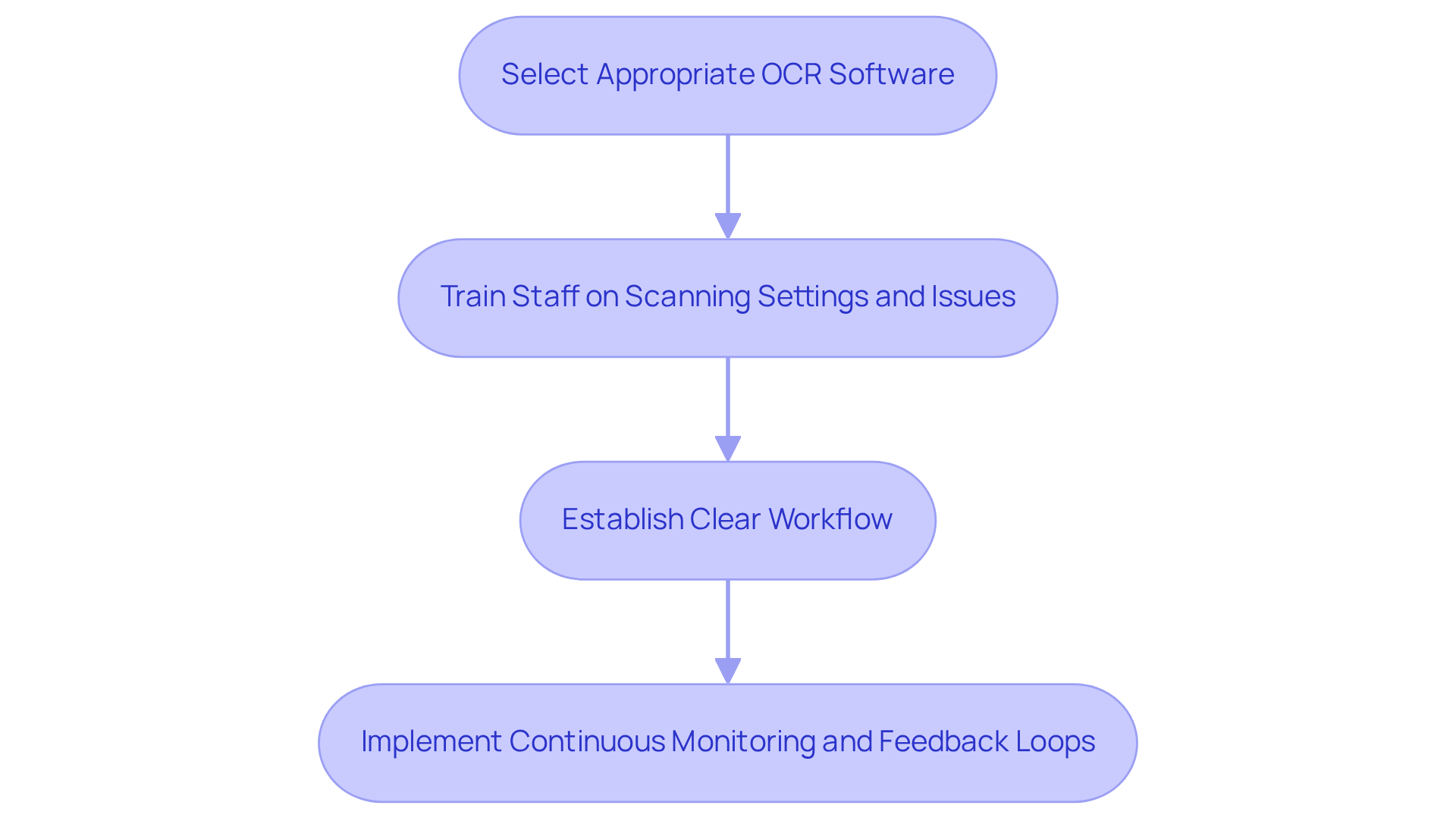
Using in title research is crucial for maximizing efficiency. First and foremost, selecting the appropriate OCR software is essential; it must effectively manage various types and formats of materials. A comprehensive evaluation of available options, including user reviews and relevant case studies, facilitates informed decision-making. For instance, organizations that have successfully integrated OCR into their workflows report significant improvements in processing speed and accuracy. Notably, open-source models often exhibit lower accuracy compared to commercial engines, underscoring the necessity of high-quality software selection.
Furthermore, effective training for staff is vital. This training should encompass optimizing scanning settings and addressing common issues, ensuring that team members are well-prepared to utilize the technology. Statistics indicate that organizations investing in thorough training programs experience a marked increase in operational efficiency, with some reporting up to a 30% reduction in manual errors.
In addition, establishing a clear workflow that incorporates OCR into existing processes enhances overall efficiency. Title researchers can implement systems where scanned files are automatically processed through OCR before undergoing accuracy reviews, significantly streamlining the workflow. However, it is crucial to recognize that challenges such as poor document quality and complex formats can hinder OCR effectiveness, making continuous monitoring and feedback loops vital.
Lastly, continuous monitoring and feedback loops are essential for assessing the effectiveness of OCR implementation. Regular assessments enable prompt modifications, ensuring that the system continues to meet evolving needs. For example, the case study on "Accelerating Loan Processing with OCR" illustrates how OCR expedites the extraction of crucial information, leading to quicker processing times and improved operational efficiency. By adhering to these best practices, title researchers can guarantee a smooth transition by using OCR for land records, fully leveraging its capabilities to enhance productivity and precision in land records management.
Overcoming Challenges in OCR Adoption for Land Records
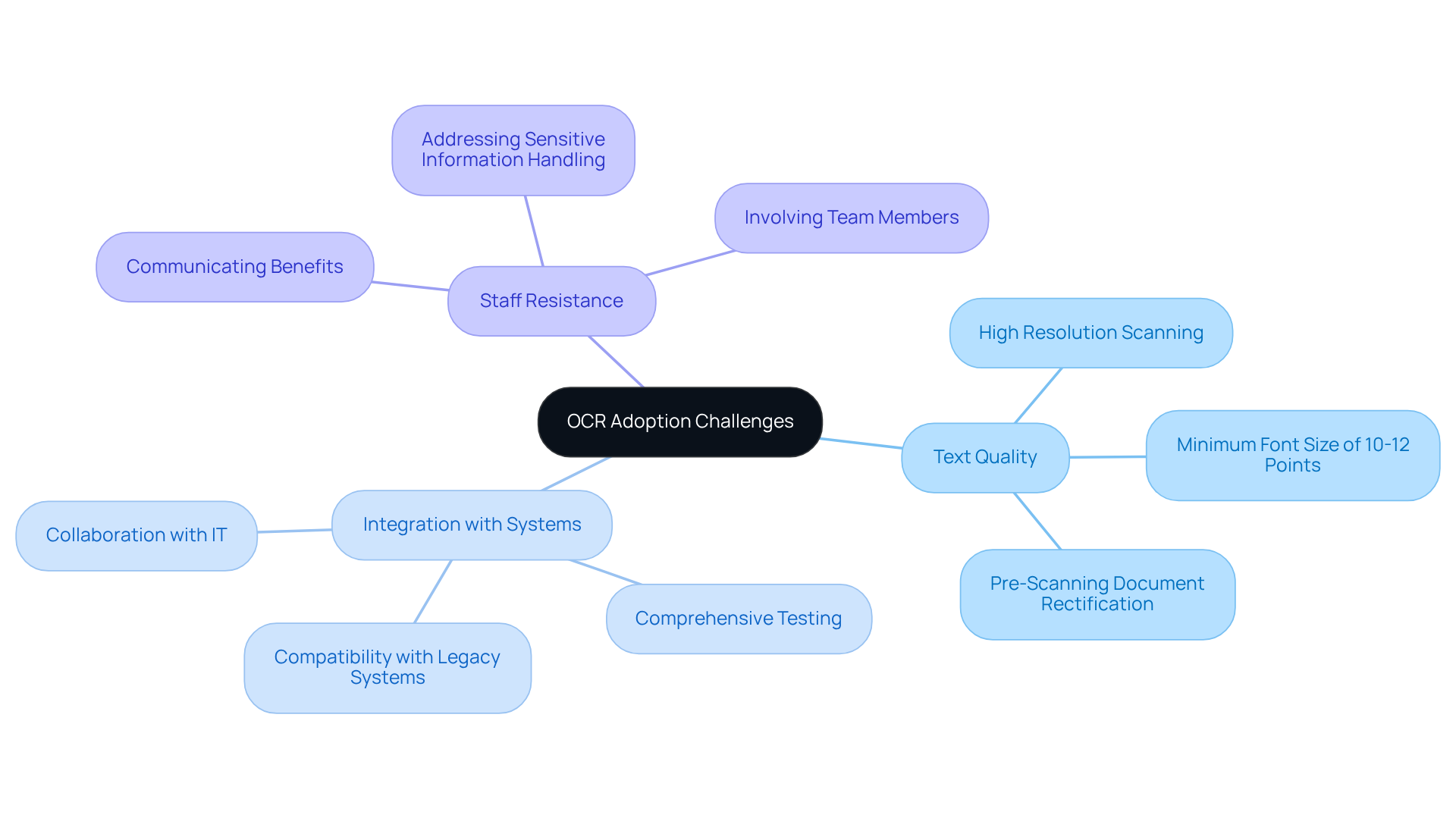
While using offers substantial benefits for management, its implementation comes with inherent challenges. A primary concern is the variability in text quality, which can significantly affect OCR accuracy. To enhance performance, title researchers must ensure documents are scanned at high resolutions—ideally 300 DPI or higher—and rectify any pre-existing issues, such as smudges or tears, prior to scanning. Additionally, maintaining a minimum font size of 10-12 points can further ensure better OCR accuracy. This approach can lead to improved data accuracy rates; advanced OCR systems can achieve up to 99% accuracy when provided with high-quality input, while IDP solutions can increase data accuracy rates up to 99.9%.
Furthermore, the integration of OCR with existing land records systems presents another challenge. Collaborating closely with IT professionals is crucial to ensure compatibility and to conduct comprehensive testing before full-scale deployment. This proactive strategy can alleviate integration issues that frequently arise when aligning OCR solutions with legacy systems.
Moreover, resistance to change among staff can impede the acceptance of new innovations. To foster this acceptance, it is essential to clearly communicate the benefits of OCR, such as increased efficiency and reduced manual data entry errors. Involving team members in the implementation process can cultivate a sense of ownership, making the transition smoother. It is also vital to address the necessity of masking and redacting sensitive information prior to scanning, as this can significantly influence staff acceptance of OCR methods.
By confronting these challenges head-on, title researchers can facilitate a successful transition by using OCR for land records technology, ultimately enhancing their workflows and improving overall efficiency in land records management.
Conclusion
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) represents a pivotal innovation in the realm of land records management, enabling the transformation of traditional document handling into a streamlined, efficient process. By digitizing extensive collections of land records, OCR significantly enhances accessibility and accuracy while reducing the time and labor required for title research. This technology is essential for modernizing workflows, ensuring that legal professionals can quickly and reliably retrieve critical information from vast archives.
The article highlights key advantages of implementing OCR in land records management, such as substantial reductions in processing times and errors. Organizations that have adopted OCR methods report impressive efficiency gains, with some achieving up to a 40% decrease in processing times and enhanced accuracy in title abstracts. However, it is crucial to acknowledge the challenges associated with OCR adoption, including variability in text quality and staff resistance to change, which can impede the successful integration of this technology.
Ultimately, embracing OCR for land records management is not merely a trend but a necessity for organizations aiming to enhance operational efficiency and compliance with legal standards. By investing in high-quality OCR systems, providing thorough training, and proactively addressing potential challenges, title researchers can leverage this technology to transform their workflows, reduce costs, and improve overall accuracy in land records management. The future of efficient land records processing lies in the successful implementation of OCR technology, marking a significant step forward in the industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Optical Character Recognition (OCR)?
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) is a technology that converts various file types, including scanned documents, PDFs, and images, into editable and searchable content.
How does OCR benefit land records management?
OCR plays a vital role in digitizing extensive collections of title materials, improving information accessibility and extraction accuracy, which is essential for title researchers.
What technology underpins modern OCR systems?
Contemporary OCR systems employ advanced machine learning algorithms to recognize and interpret complex legal language and various document formats.
What are the advantages of using OCR for land records management systems?
Using OCR streamlines workflows, reduces manual entry errors, and results in faster and more reliable property ownership verification.
What is the projected growth of the global OCR market?
The global OCR market is projected to reach $3.72 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate of 13.6%.
How does OCR improve operational efficiency in the real estate sector?
Successful implementations of OCR can automate information extraction processes up to ten times faster than manual methods, reducing labor costs and improving compliance with regulatory standards.
Can you provide an example of OCR effectiveness in land records management?
Arbor achieved a straight-through processing rate exceeding 95% and over 99% accuracy in data extraction after adopting OCR techniques, demonstrating its practical effectiveness.
What challenges are associated with using OCR?
Potential challenges include issues with handwriting recognition and low-resolution images, which can negatively impact OCR performance.




