Overview
The article emphasizes the critical role of mastering Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and integrating land records in achieving successful title research. It highlights that by effectively merging spatial and non-spatial data, researchers can significantly enhance efficiency, accuracy, and decision-making in property assessments. Furthermore, it outlines strategies for implementing GIS technology while addressing common challenges encountered during the integration process, ultimately reinforcing the reliability of these solutions.
Introduction
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have fundamentally transformed the access and analysis of property information, serving as a formidable tool for title researchers as they navigate the intricate landscape of land records. By integrating GIS with land records, researchers can streamline workflows, enhance accuracy, and uncover insights that were once challenging to obtain. However, the path to mastering this integration is not without its challenges. What strategies can effectively overcome these obstacles and fully harness the potential of GIS in title research?
Understand GIS and Land Record Integration
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) serve as powerful instruments that empower users to visualize, analyze, and interpret spatial information effectively. In the realm of ownership research, GIS and land record integration combine various land records—ownership details, property boundaries, and historical data—into a cohesive framework. This seamless integration allows title researchers to swiftly access and analyze property information within a geographic context, thereby facilitating more efficient title searches. Understanding the mechanics of GIS and land record integration is crucial for harnessing its full potential in .
Key components of GIS include:
- Spatial Data: Information concerning the location and shape of physical features on the earth's surface.
- Non-Spatial Information: Attributes linked to spatial data, such as ownership details and legal descriptions.
- Data Integration: The process of amalgamating spatial and non-spatial data to produce comprehensive datasets, enabling enhanced decision-making.
By comprehending these concepts, property researchers can fully appreciate how GIS and land record integration amplifies their capacity to manage and interpret land records, ultimately resulting in more precise and timely research outcomes.
Implement GIS Technology in Title Research
To implement GIS technology in title research effectively, follow these steps:
- Identify Your Needs: Assess the specific requirements of your title research process. Identify what kinds of information you require to integrate and how GIS can tackle your challenges.
- Choose the Right GIS Software: Select a GIS platform that aligns with your needs. Popular options include ArcGIS, QGIS, and MapInfo. Consider factors such as ease of use, available features, and integration capabilities with existing systems.
- Gather Information: Collect the necessary spatial and non-spatial details. This may include land records, property boundaries, and historical documents. Ensure that the information is accurate and current.
- Train Your Team: Provide training for your team on how to use the chosen GIS software effectively. This may involve workshops, online courses, or hands-on practice sessions.
- Create a GIS Database: Arrange your information into a GIS database, ensuring that it is structured for easy access and analysis. This may involve digitizing paper records and integrating them into the GIS system.
- Start Mapping: Begin creating maps that visualize the data. Use GIS tools to overlay different datasets, allowing for and insights into property ownership and boundaries.
By adhering to these steps, researchers can implement GIS technology, enhancing their research capabilities and improving overall efficiency. As noted in industry reports, the global GIS software market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 16.2% from 2024 to 2033, highlighting the increasing reliance on GIS solutions. Furthermore, as Jack Dangermond stated, "The application of GIS is limited only by the imagination of those who use it," emphasizing the importance of selecting the right platform for success. Successful implementations in title research have demonstrated that GIS and land record integration not only improves efficiency but also enhances the accuracy of property assessments and ownership verifications.
Integrate GIS with Land Records for Enhanced Efficiency
To effectively integrate GIS with land records, it is essential to consider the following strategies:
- Standardize Information Formats: Adhering to uniform information formats across all GIS records is crucial. This practice not only simplifies integration but also reduces errors during information entry, ensuring consistency and reliability. As noted by the Harbinger Content Team, "GIS has become an indispensable tool in the field of land acquisition, offering precise and comprehensive analysis."
- Utilize APIs for Information Exchange: Implementing Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) facilitates between GIS and land record management platforms. This integration allows for real-time updates, ensuring access to the most current information available. The benefits of using APIs include improved operational efficiency and enhanced customer experiences, which are vital for effective land record management.
- Create Interactive Maps: Developing interactive maps significantly enhances user experience by allowing queries based on various parameters, such as location, parcel identification number, or ownership history. This functionality expedites the research process and enhances access to essential information.
- Automate Data Updates: Establishing automated procedures for refreshing land records within the GIS framework is essential. This ensures that any changes in ownership or property details are reflected in real-time, thereby maintaining data accuracy and integrity.
- Collaborate with Stakeholders: Engaging with land service professionals, surveyors, and local government agencies is crucial to ensure that the GIS platform meets the diverse needs of all parties involved in land record management.
By adopting GIS and land record integration, title researchers can significantly enhance their efficiency, reduce errors, and improve the overall quality of their research.
Troubleshoot Common Implementation Challenges
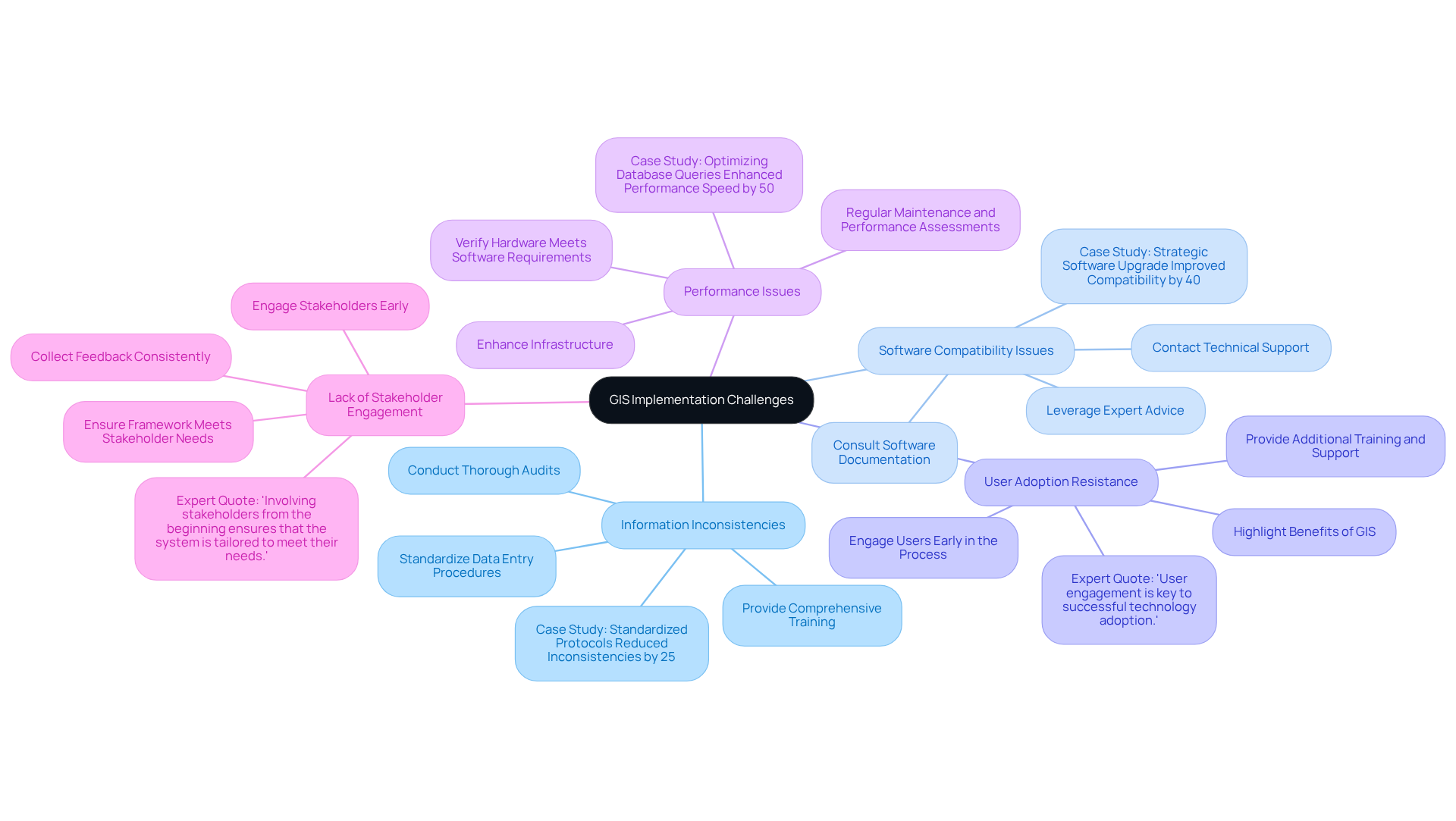
Implementing GIS technology presents several challenges that require careful attention. To effectively address these common issues, consider the following strategies:
- Information Inconsistencies: Discrepancies in information can undermine the effectiveness of GIS systems. Studies indicate that inconsistencies can affect up to 30% of GIS datasets, leading to significant errors in analysis and decision-making. Conducting a thorough audit is essential to identify the sources of these inconsistencies. Standardizing information entry procedures and providing comprehensive training for team members on best practices can significantly reduce errors. As industry specialists emphasize, addressing information quality is crucial for enhancing the utility of GIS applications. A successful project in [specific case study] demonstrated that implementing standardized data protocols reduced inconsistencies by 25%.
- Software Compatibility Issues: Ensuring seamless integration of GIS software with existing setups is vital. If integration problems arise, consult the software documentation or contact technical support for assistance. Many organizations have successfully navigated these challenges by leveraging expert advice and utilizing compatible software solutions. A notable example is [specific case study], where a strategic software upgrade improved compatibility and reduced integration time by 40%.
- User Adoption Resistance: Resistance to adopting new technology can hinder GIS implementation. To overcome this barrier, provide additional training and support to team members. Highlight the benefits of GIS, such as improved workflows and reduced errors, to encourage buy-in. Engaging users early in the process fosters a sense of ownership and facilitates smoother transitions. As [expert name] states, "User engagement is key to successful technology adoption."
- Performance Issues: Slow or unresponsive GIS platforms can frustrate users. To address performance issues, verify that your . Enhancing infrastructure or refining your database can lead to significant improvements in responsiveness. Regular maintenance and performance assessments are also recommended to ensure ongoing efficiency. For instance, [specific case study] demonstrated that optimizing database queries enhanced performance speed by 50%.
- Lack of Stakeholder Engagement: Engaging stakeholders early in the GIS implementation process is crucial. Collecting feedback and ensuring that the framework meets their needs can improve support and facilitate smoother adoption. Consistent communication and collaboration with stakeholders assist in aligning the GIS framework with organizational objectives. As noted by [expert name], "Involving stakeholders from the beginning ensures that the system is tailored to meet their needs."
By proactively addressing these challenges, title researchers can ensure a successful implementation of GIS and land record integration, ultimately leading to enhanced efficiency and accuracy in their workflows.
Conclusion
Mastering the integration of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) with land records is essential for title research success. This powerful combination streamlines the research process and enhances the accuracy and efficiency of property assessments. By leveraging GIS technology, title researchers can access and analyze vital information in a geographical context, leading to more informed decision-making.
The article outlines several key strategies for implementing GIS in title research, including:
- Identifying specific needs
- Choosing appropriate software
- Creating a structured GIS database
It emphasizes the importance of:
- Standardizing information formats
- Utilizing APIs for seamless data exchange
- Developing interactive maps to improve user experience
Furthermore, addressing common challenges such as information inconsistencies and user resistance is crucial for ensuring successful GIS integration.
In conclusion, the integration of GIS with land records represents a transformative approach to title research that significantly improves operational efficiency and data accuracy. Embracing these technologies prepares researchers for current demands and positions them for future advancements in the field. By taking proactive steps towards implementation and continuously engaging with stakeholders, title researchers can unlock the full potential of GIS, ultimately leading to greater success in their endeavors.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in land record integration?
GIS serves as a powerful tool that enables users to visualize, analyze, and interpret spatial information effectively, particularly in ownership research by integrating various land records into a cohesive framework.
What types of information are combined in GIS and land record integration?
GIS and land record integration combine spatial data, such as property boundaries and physical features, with non-spatial information, including ownership details and legal descriptions.
How does GIS enhance title research?
The integration of GIS with land records allows title researchers to quickly access and analyze property information within a geographic context, facilitating more efficient title searches.
What are the key components of GIS?
The key components of GIS include spatial data (location and shape of physical features), non-spatial information (attributes linked to spatial data), and data integration (the amalgamation of spatial and non-spatial data to create comprehensive datasets.)
Why is understanding GIS and land record integration important for property researchers?
Understanding these concepts allows property researchers to fully appreciate how GIS enhances their ability to manage and interpret land records, leading to more precise and timely research outcomes.




