Overview
To effectively locate mineral deeds, one must adopt a systematic approach that encompasses:
- Identifying the property
- Visiting the county recorder's office
- Examining the chain of title
Understanding the nuances of mineral deeds is crucial. Furthermore, utilizing available resources, including online databases and legal assistance, can aid in navigating challenges such as:
- Insufficient documentation
- Title discrepancies
Consequently, this approach not only ensures clarity in ownership but also maximizes financial benefits.
Introduction
Understanding the intricacies of mineral deeds is essential for landowners and real estate professionals alike. These documents govern the rights to valuable resources beneath the surface, making accurate title research crucial. The ability to locate and interpret mineral deeds can significantly impact property value and income potential, particularly in resource-rich areas. However, navigating the complexities of mineral rights can lead to confusion and disputes if not approached correctly. Therefore, how can individuals ensure they effectively locate these critical documents while avoiding common pitfalls in the process?
Understand Mineral Deeds and Their Importance
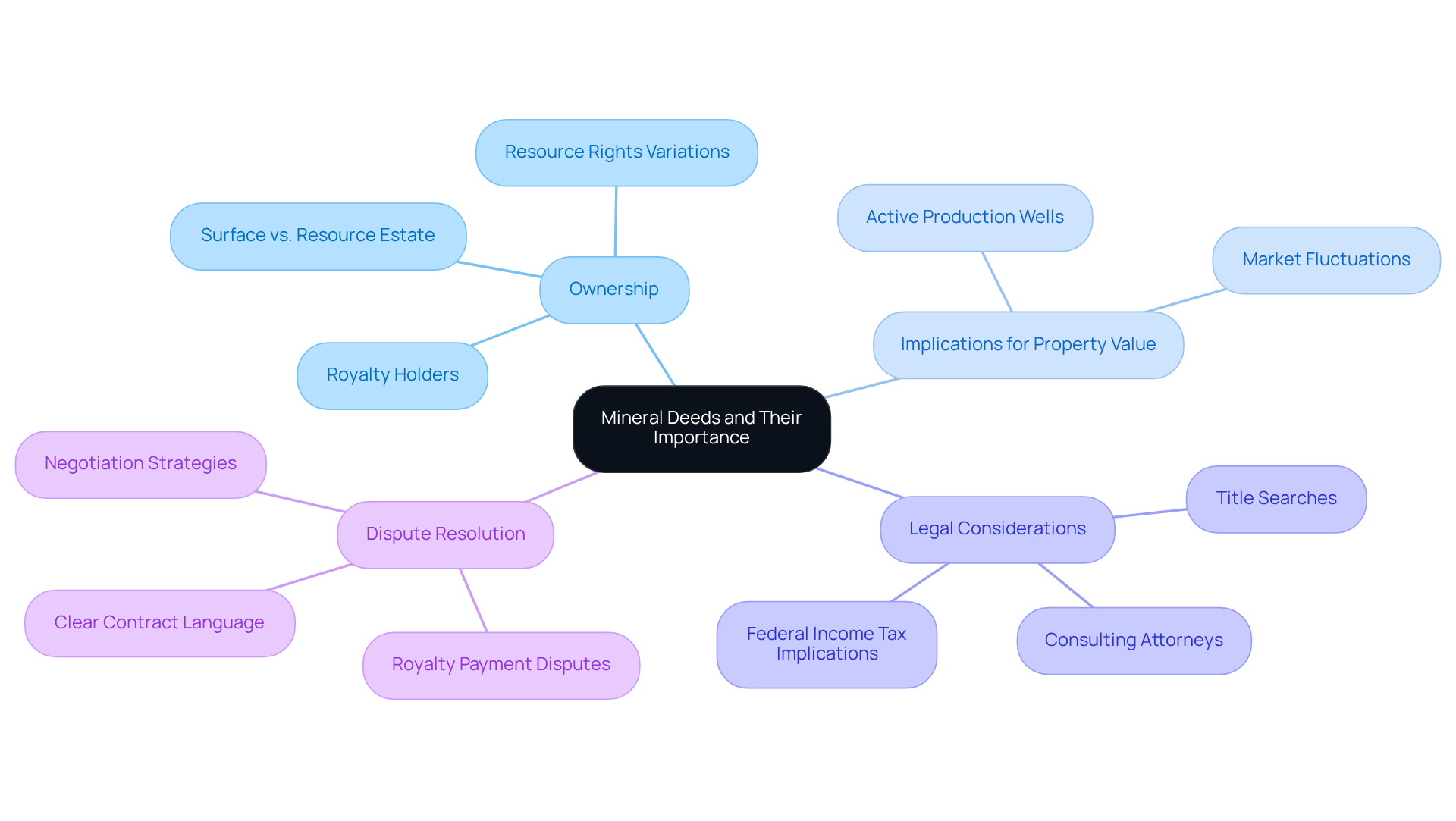
Deeds related to resources are essential legal documents that convey control over the substances found beneath a property, playing a significant role in establishing who has the authority to extract materials such as oil, gas, and other resources. For landowners and real estate professionals, understanding these deeds is crucial, as they can significantly impact property value and the potential income generated from resource extraction. In Texas, the complexity of resource entitlement is underscored by the fact that there were 12.6 million royalty holders in 2021, a consequence of the fragmentation of resource ownership.
When examining resource rights, it is essential to recognize that property deeds can vary considerably in the rights they confer. These variations may encompass permissions for extraction, leasing arrangements, or entitlements to royalties. A clear understanding of the terminology and implications related to resource deeds not only aids in the search process but also provides real estate professionals with the knowledge of how to locate mineral deeds and navigate the complexities of resource rights. Disputes over royalty payments frequently arise from unclear contract language and misinterpretations, making it vital for professionals to be well-informed.
The impact of resource deeds extends beyond mere ownership; they can enhance property value, particularly in areas with , such as Midland County and the Eagle Ford Shale, where the potential for income generation is substantial. Real estate experts often encounter situations where surface, resource, and executive entitlements are held by different parties, necessitating a comprehensive understanding of these distinctions to prevent disputes and ensure equitable negotiations. As Nixon Daughtrey notes, under Texas law, priority is assigned to the resource estate over its surface equivalent, underscoring the importance of resource ownership.
Expert opinions emphasize that a precise assessment of resource entitlements is essential, as market fluctuations can significantly influence their value. Engaging with experienced lawyers and conducting thorough title searches are recommended actions for individuals involved in rights management, ensuring clarity in ownership and maximizing the financial benefits associated with deeds. Furthermore, resource owners must be cognizant of the federal income tax implications on royalty payments, which can affect their overall financial strategy.
Conduct a Comprehensive Mineral Deed Search
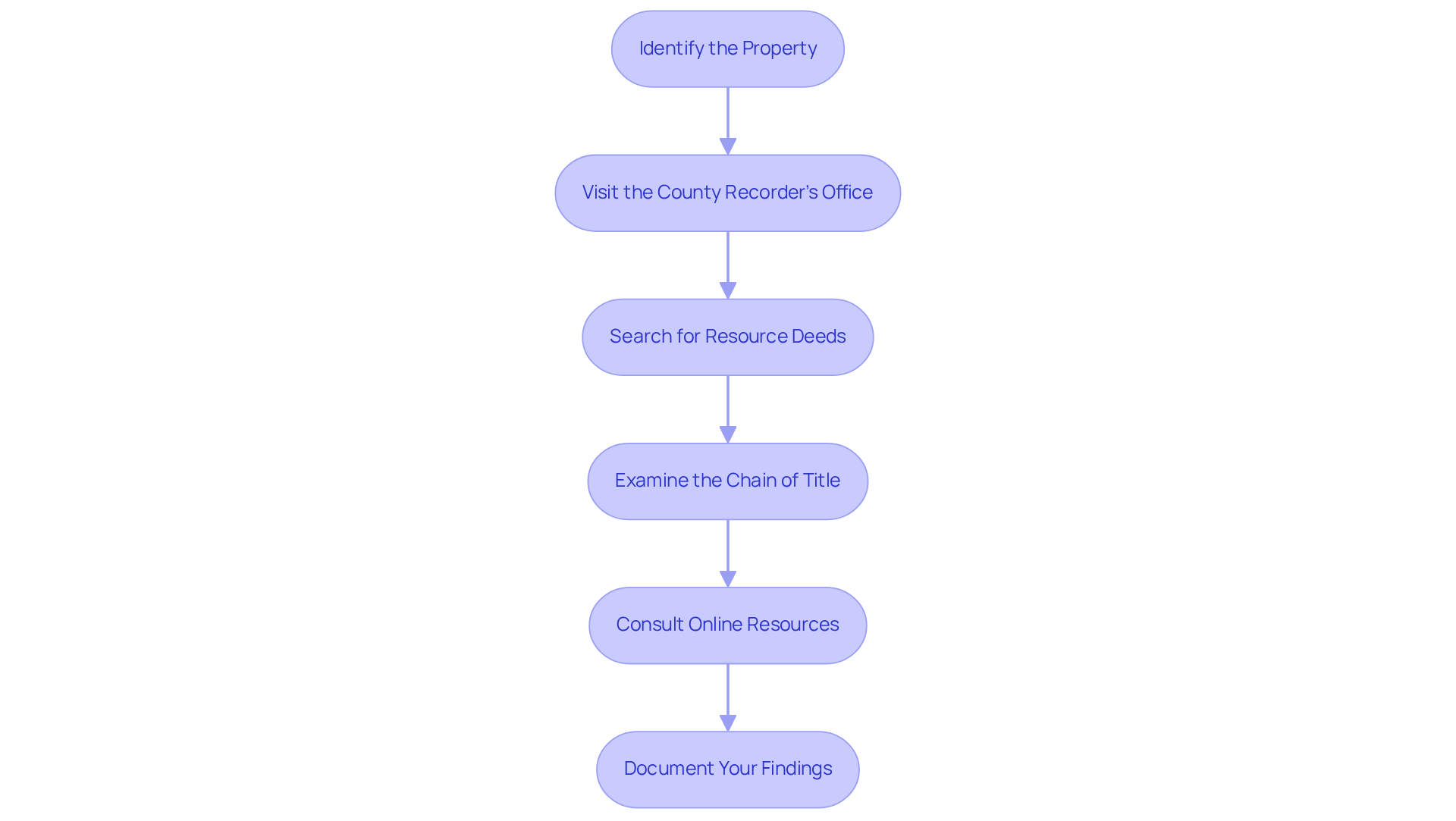
To conduct a comprehensive mineral deed search, it is essential to follow these steps:
- Identify the Property: Begin by determining the legal description of the property. This information is typically accessible on the property deed or through local tax documentation. A precise legal description is crucial for accurately identifying resource rights.
- Visit the County Recorder's Office: Proceed to the county recorder's office where the property is located. This office maintains public documents, including property deeds. Many counties also provide online databases for easier access to these records.
- Search for Resource Deeds: Utilize the legal description to understand how to locate mineral deeds. Focus on documents that indicate the transfer of resource ownership, paying close attention to the dates and names involved in the transactions. This step is vital as it establishes a , defined as a title free from claims for any individual who has held an estate in land for 40 years or more. Remember, the root of title must be a title transaction recorded at least 40 years prior to the time when marketability is being assessed.
- Examine the Chain of Title: Trace the ownership history of the mineral claims by reviewing the chain of title. This examination will illuminate how the rights have changed hands over time and help identify any potential issues. The Marketable Record Title Act (MRTA) simplifies this process by allowing a focus on the 'postroot' documents while identifying exceptions in the 'preroot' documents. MRTA serves as a statute of limitations, eliminating ancient defects in title unless exceptions apply.
- Consult Online Resources: Utilize online platforms such as the Bureau of Land Management's Mineral & Land Records System (MLRS) to access additional documents and maps that may assist in your search. These resources can provide valuable context and supplementary information.
- Document Your Findings: Maintain detailed notes of your findings, including document numbers, dates, and any discrepancies encountered. This documentation will prove invaluable for future reference or if consultation with a legal expert is necessary. A comprehensive account will also aid in ensuring adherence to MRTA, which serves as a statute of limitations, removing outdated defects in title unless exceptions apply.
Troubleshoot Common Issues in Mineral Deed Searches
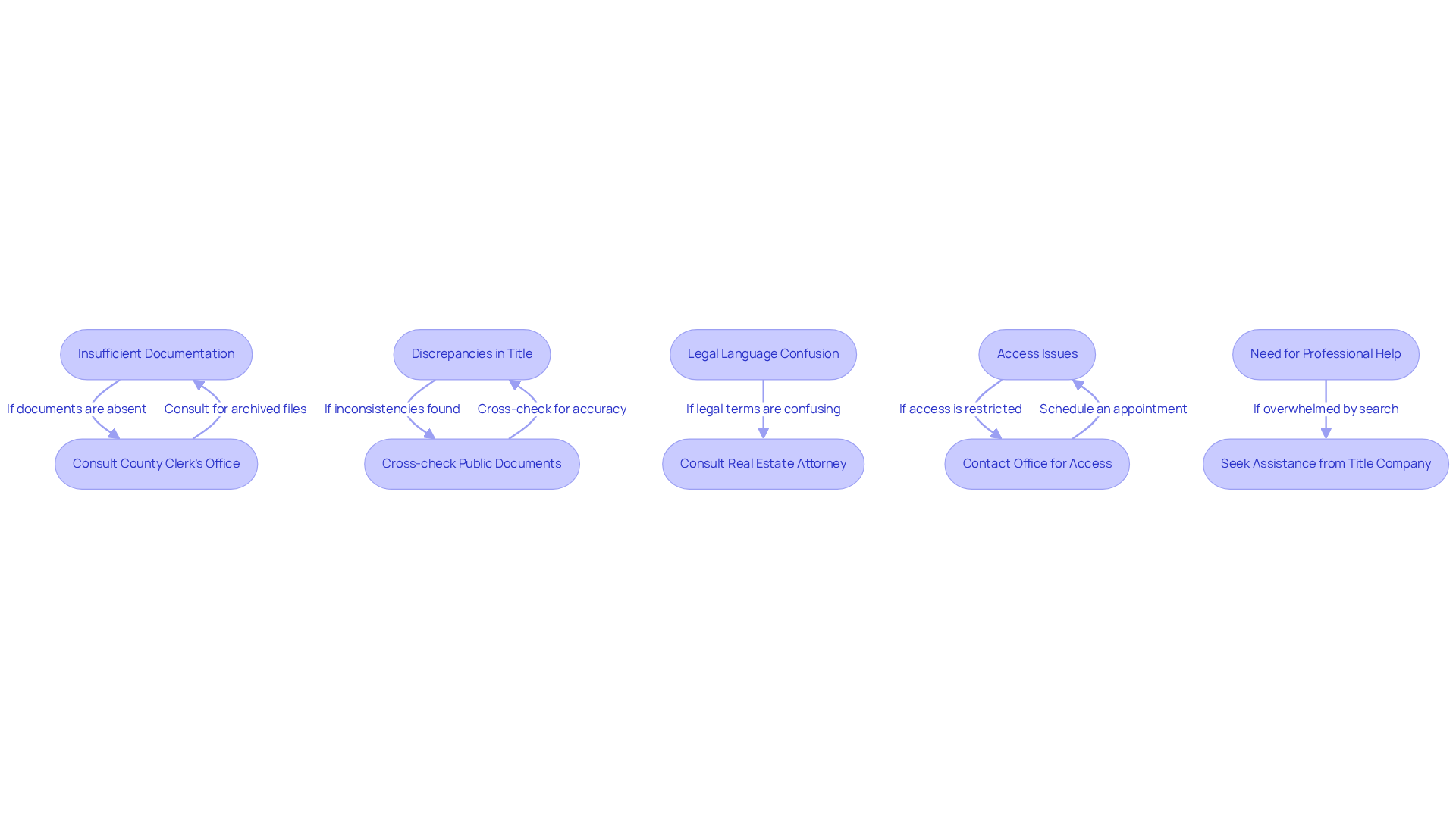
When conducting a resource deed search, understanding how to can help overcome several typical challenges that may arise. Here’s how to effectively troubleshoot them:
- Insufficient Documentation: Should documents appear absent or lacking, it is advisable to consult the county clerk's office for archived files or additional resources that may not be accessible online. Statistics indicate that public documentation for mineral deeds frequently lacks completeness, with some counties reporting that up to 30% of files are unfiled or improperly archived. Thus, this step is essential.
- Discrepancies in Title: If inconsistencies in title names or dates are encountered, it is prudent to cross-check with other public documents, such as tax assessments or probate files, to clarify the accurate title. This method has proven effective in resolving property disputes, as evidenced by a case where a title search revealed a 15-year-old error in property documentation that was corrected through meticulous cross-referencing.
- Legal Language Confusion: Mineral deeds often encompass complex legal terminology. Nixon Daughtrey, a lawyer specializing in real estate, asserts, "Comprehending property ownership nuances is crucial for maximizing its benefits." If the language proves challenging, consulting a real estate attorney or a title research professional can provide guidance on how to locate mineral deeds accurately.
- Access Issues: Should access to certain records be hindered by office hours or restrictions, it is advisable to contact the office in advance to schedule an appointment or inquire about remote access options. This proactive approach can save time and frustration, as many offices now provide online appointment scheduling.
- Need for Professional Help: If the search for how to locate mineral deeds becomes overwhelming or legal challenges arise, do not hesitate to seek assistance from a title company or a landman who specializes in this area. Their expertise can streamline the process and ensure accuracy, ultimately conserving time and resources. Utilizing services like Parse AI can further enhance efficiency in extracting essential information from title documents.
Conclusion
Understanding mineral deeds is crucial for anyone engaged in real estate, particularly in areas where resource extraction significantly impacts property value. These legal documents not only define ownership rights but also affect the potential income derived from valuable resources beneath the land. By mastering the intricacies of mineral deeds, landowners and real estate professionals can adeptly navigate the complex landscape of resource rights, making informed decisions that safeguard their investments.
This article outlines a clear, step-by-step approach to locating mineral deeds, underscoring the importance of thorough documentation, comprehension of legal terminology, and leveraging both county resources and online platforms. Key strategies include:
- Accurately identifying the property
- Examining the chain of title
- Troubleshooting common issues that may arise during the search process
By adhering to these guidelines, individuals can effectively uncover essential information regarding mineral rights, ensuring clarity in ownership.
Ultimately, the significance of mineral deeds transcends mere documentation; it encompasses the financial implications and legal complexities that can emerge in resource management. Engaging with experienced professionals and conducting diligent searches not only protects investments but also maximizes the benefits associated with mineral rights. For those involved in real estate, taking proactive steps to understand and locate mineral deeds is not just advisable—it is essential for ensuring long-term success in a resource-rich environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are mineral deeds and why are they important?
Mineral deeds are legal documents that convey control over the resources found beneath a property, such as oil and gas. They are important because they establish who has the authority to extract these materials, impacting property value and potential income from resource extraction.
How do mineral deeds affect property value?
Mineral deeds can enhance property value, especially in areas with active production wells. The potential for income generation from resource extraction can significantly increase the overall worth of a property.
What variations can exist in property deeds related to resources?
Property deeds can vary in the rights they confer, including permissions for extraction, leasing arrangements, or entitlements to royalties. Understanding these variations is crucial for navigating resource rights.
What issues can arise from mineral deeds?
Disputes over royalty payments often occur due to unclear contract language and misinterpretations. It is vital for real estate professionals to be well-informed to prevent such disputes.
What is the significance of resource ownership in Texas?
In Texas, resource ownership is prioritized over surface ownership under state law. This highlights the importance of understanding the distinctions between surface, resource, and executive entitlements to prevent disputes.
What should individuals involved in rights management do to ensure clarity in ownership?
Individuals should engage with experienced lawyers and conduct thorough title searches to ensure clarity in ownership and maximize the financial benefits associated with mineral deeds.
Are there tax implications for resource owners regarding royalty payments?
Yes, resource owners should be aware of the federal income tax implications on royalty payments, as these can affect their overall financial strategy.




