Introduction
Understanding liens on property is essential for anyone involved in real estate, as these legal claims can significantly impact ownership rights and property transactions. A lien serves as a safeguard for lenders, ensuring that they can reclaim property if debts remain unpaid. With various types of liens, including mortgage, tax, and judgment liens, each comes with its own set of legal implications and complexities.
This article delves into the nature of property liens, the processes for placing and removing them, and their implications for property owners, providing critical insights for title researchers and real estate professionals navigating this intricate landscape. By exploring these aspects, stakeholders can better understand the importance of maintaining clear title and managing obligations associated with liens, ultimately protecting their investments and interests in real estate.
Understanding the Concept of a Lien on Property
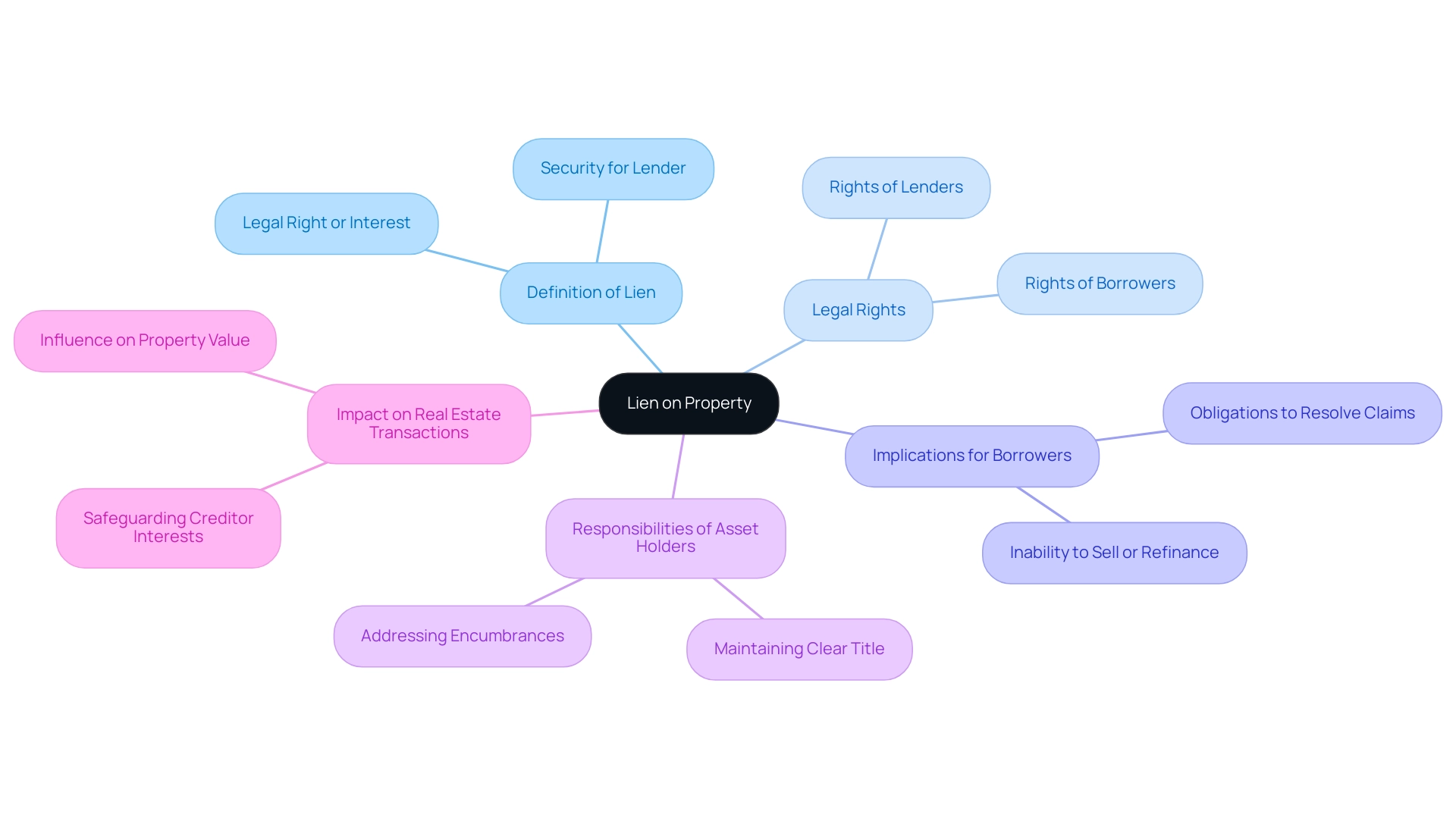
A claim on an asset raises the question of what does it mean to place a lien on property, which is a legal right or interest that a lender or a third party holds in the asset until is fulfilled. Liens serve as a form of security for the lender, which brings up the question of what does it mean to place a lien on property if the borrower fails to meet their obligations. Comprehending encumbrances is essential for real estate possession, as they can greatly influence the rights of landholders.
For example, if an asset is under a claim, it cannot be sold or refinanced without resolving the claim first. This legal mechanism is essential in real estate dealings, as it safeguards the interests of creditors while also placing responsibilities on asset holders to maintain clear title to their possessions.
Exploring Different Types of Property Liens
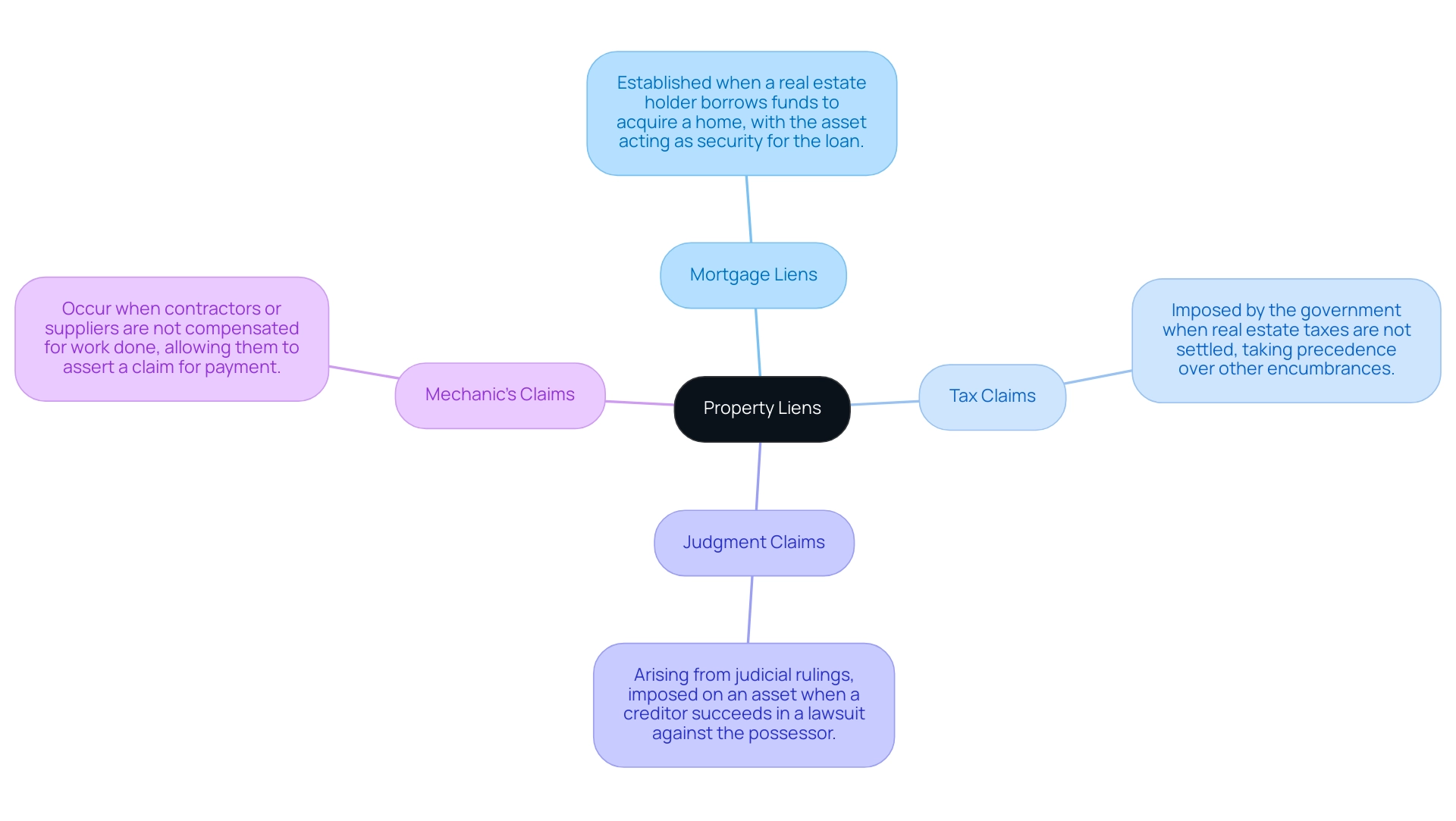
There are multiple kinds of financial claims, each serving different functions and emerging from various situations. The most common types include:
- Mortgage Liens: These are established when a real estate holder borrows funds to acquire a home, with the asset acting as security for the loan.
- Tax Claims: Imposed by the government when real estate taxes are not settled, tax claims take precedence over other forms of encumbrances.
- Judgment Claims: Arising from judicial rulings, these claims are imposed on an asset when a creditor succeeds in a lawsuit against the possessor.
- Mechanic’s Claims: These occur when contractors or suppliers are not compensated for work done on the premises, permitting them to assert a claim to ensure payment.
Each category of claim has specific legal implications and processes for resolution, making it vital for title researchers and landowners to understand their rights and obligations related to these assertions.
The Process of Placing a Lien on Property
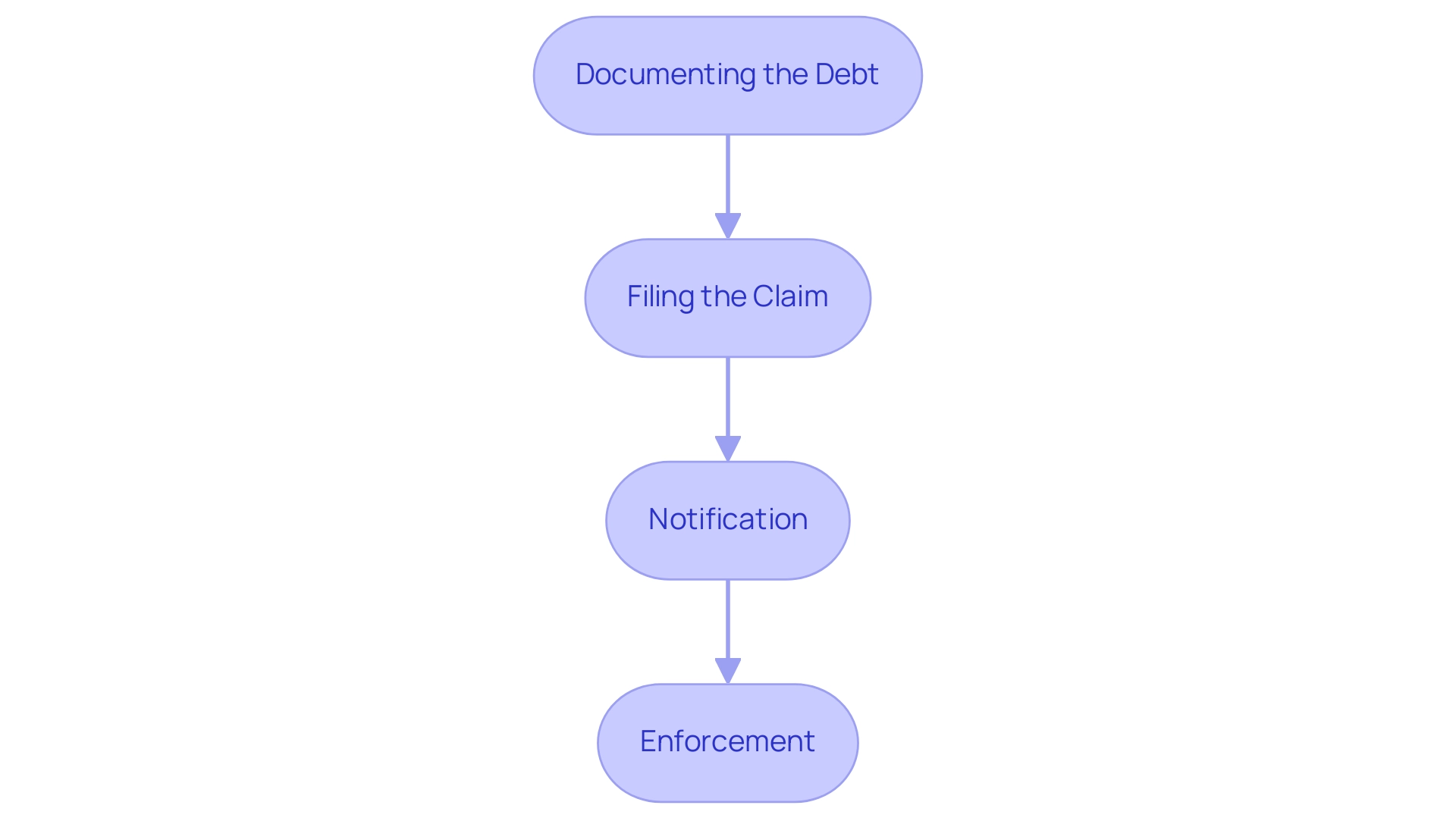
The procedure of imposing a claim on real estate often leads to inquiries about what does it mean to place a lien on property.
- Documenting the Debt: The creditor must document the debt owed, including the amount and the terms of repayment.
- Filing the Claim: The creditor submits a claim with the appropriate government office, often the county recorder's office. This filing establishes a public record of the claim against the asset, illustrating what does it mean to place a lien on property.
- Notification: In certain areas, the property owner must be informed of the claim placement.
- Enforcement: If the debt remains unpaid, the creditor may execute the claim, which could lead to foreclosure proceedings.
Understanding what does it mean to place a lien on property is essential for title researchers and real estate professionals, particularly when utilizing advanced machine learning tools from Parse AI for automated document processing and title research. With features such as OCR technology and interactive labeling, title researchers can efficiently document claims, ensuring compliance with legal requirements while significantly reducing the time spent on manual data entry. For example, Parse Ai's OCR technology can swiftly extract relevant details from legal documents, allowing researchers to focus on analysis rather than paperwork.
Moreover, Harbinger Land's proficiency in securing precise leases and performing enhances the application of Parse Ai's tools, as they offer and understanding to maneuver through the intricacies of real estate ownership and claims effectively.
Implications of Liens for Property Owners
Understanding what does it mean to place a lien on property is essential for , as it can have substantial effects.
- Impact on Sale or Transfer: An asset with an active claim cannot be sold or transferred without addressing the claim, which can complicate transactions.
- Credit Impact: Liens can negatively influence the individual's credit score, as they signify outstanding debt obligations.
- Possible Foreclosure: If a claim is not settled, the creditor may start foreclosure actions, resulting in the loss of the asset.
- Legal Expenses: Settling claims can result in judicial charges and extra expenses, making it crucial for landowners to tackle any claims swiftly.
Understanding what does it mean to place a lien on property is vital for maintaining clear title and ensuring compliance with legal obligations.
How to Remove a Lien from Property
Eliminating a claim from real estate usually entails multiple important steps that necessitate thoughtful evaluation:
- Paying Off the Debt: The most straightforward method to eliminate a claim is to pay off the debt that the claim secures. Once the debt is settled, the creditor is required to submit a release document, which officially removes the claim from the asset.
- Negotiating with the Creditor: In some situations, negotiating a settlement with the creditor can yield favorable results, allowing for the claim to be removed for less than the full amount owed. This process often involves discussing payment terms and the possibility of a reduced settlement amount.
- Demonstrating the Claim is Invalid: If a claim has been imposed in error or is otherwise considered invalid, landholders have the right to contest it in court. This may involve collecting evidence and documentation to support their claim.
- Filing for Bankruptcy: In certain situations, filing for bankruptcy can eliminate specific types of claims, offering a means of relief for property owners facing significant financial difficulties.
Each of these methods carries its own legal implications, and costs can vary widely. For instance, Barbara Billiot Stage, a real estate attorney in Rockledge, FL, notes that any payments made towards a claim are often first applied to interest and fees rather than the principal debt. Consequently, unless the total amount demanded is paid, the owner remains past due on their assessments. Legal fees related to removal can accumulate quickly, making it essential to seek professional legal advice. Seeking advice from a title agent or lawyer can offer invaluable support on the most effective methods for debt removal and navigating the complexities of selling assets with existing encumbrances. Furthermore, when selling a home with a claim, it is essential to be transparent with your real estate agent to enhance the marketing of the asset. A case study regarding HOA liens emphasizes what does it mean to place a lien on property, highlighting that homeowners who miss payments may encounter significant fees for lien removal, even after settling their original debts, underscoring the importance of counsel in these matters. Furthermore, understanding , which range from 10.0 - 9.0 for Superb to 1.9 - 1.0 for Extreme Caution, can help property owners evaluate what does it mean to place a lien on property and determine the quality of legal representation they may need in lien-related issues.
Conclusion
Liens on property represent a critical aspect of real estate that can profoundly influence ownership rights and the ability to engage in transactions. Understanding the nature of liens, from mortgage to tax and judgment liens, is essential for property owners and real estate professionals alike. Each type of lien carries unique implications and processes, which can complicate property sales, affect credit scores, and potentially lead to foreclosure if not addressed promptly.
The process of placing and removing liens involves several key steps that must be navigated carefully. From documenting debts to negotiating settlements and proving the validity of a lien, property owners must be proactive in managing these legal claims. The role of legal counsel and title agents cannot be overstated, as they provide necessary guidance through the complexities of lien management and ensure compliance with legal obligations.
Ultimately, maintaining clear title and actively addressing any existing liens is imperative for protecting investments in real estate. By arming themselves with knowledge and seeking the appropriate professional support, stakeholders can navigate the complexities of property liens effectively, safeguarding their interests and enhancing their ability to conduct successful transactions. Understanding and managing liens is not just a legal necessity; it is a fundamental aspect of responsible property ownership.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a lien on property?
A lien is a legal right or interest that a lender or a third party holds in an asset until a debt obligation is fulfilled. It serves as a form of security for the lender.
What happens if a borrower fails to meet their obligations regarding a lien?
If the borrower fails to meet their obligations, the creditor may enforce the lien, which could lead to foreclosure proceedings.
Why is understanding encumbrances important for real estate possession?
Understanding encumbrances is crucial because they can significantly influence the rights of landholders, affecting their ability to sell or refinance the property.
What are the common types of liens?
Common types of liens include: 1. Mortgage Liens: Established when borrowing funds to acquire real estate. 2. Tax Claims: Imposed by the government for unpaid real estate taxes. 3. Judgment Claims: Resulting from judicial rulings against the property owner. 4. Mechanic’s Claims: Arising from unpaid work by contractors or suppliers.
What is the process for placing a lien on property?
The process includes: 1. Documenting the debt owed. 2. Filing the claim with the appropriate government office. 3. Notifying the property owner in certain areas. 4. Enforcing the claim if the debt remains unpaid.
How can a lien impact the sale or transfer of property?
An asset with an active lien cannot be sold or transferred without resolving the claim, complicating transactions.
What are the potential consequences of having a lien on property?
Consequences include a negative impact on credit scores, possible foreclosure, and legal expenses associated with settling the claim.
How can a property owner eliminate a lien?
A lien can be eliminated by: 1. Paying off the debt. 2. Negotiating a settlement with the creditor. 3. Demonstrating that the claim is invalid. 4. Filing for bankruptcy in certain situations.
What should property owners consider when dealing with liens?
Property owners should seek professional legal advice to navigate the complexities of lien removal and understand the implications of selling assets with existing claims.




