Overview
The article offers a comprehensive guide on the process of abstracting for mineral rights, emphasizing the critical steps necessary to establish clear ownership and address potential issues. It begins by highlighting the significance of accurate title research, which is foundational to successful transactions.
Furthermore, the article outlines essential components and common challenges encountered in this process. It also presents effective troubleshooting strategies, underscoring the importance of thorough documentation and meticulous record-keeping.
Consequently, these practices are vital for ensuring successful mineral rights transactions.
Introduction
The complexities of mineral rights ownership often leave many property owners and investors navigating a maze of legal intricacies. Understanding the process of abstracting for mineral rights is not just beneficial; it is essential for ensuring clear ownership and preventing costly disputes. Furthermore, with various common pitfalls and challenges that can arise, how can one effectively manage the abstracting process to safeguard their interests?
This guide delves into a step-by-step approach to abstracting mineral rights, illuminating the key components and troubleshooting strategies that will empower readers to navigate this critical aspect of property management with confidence.
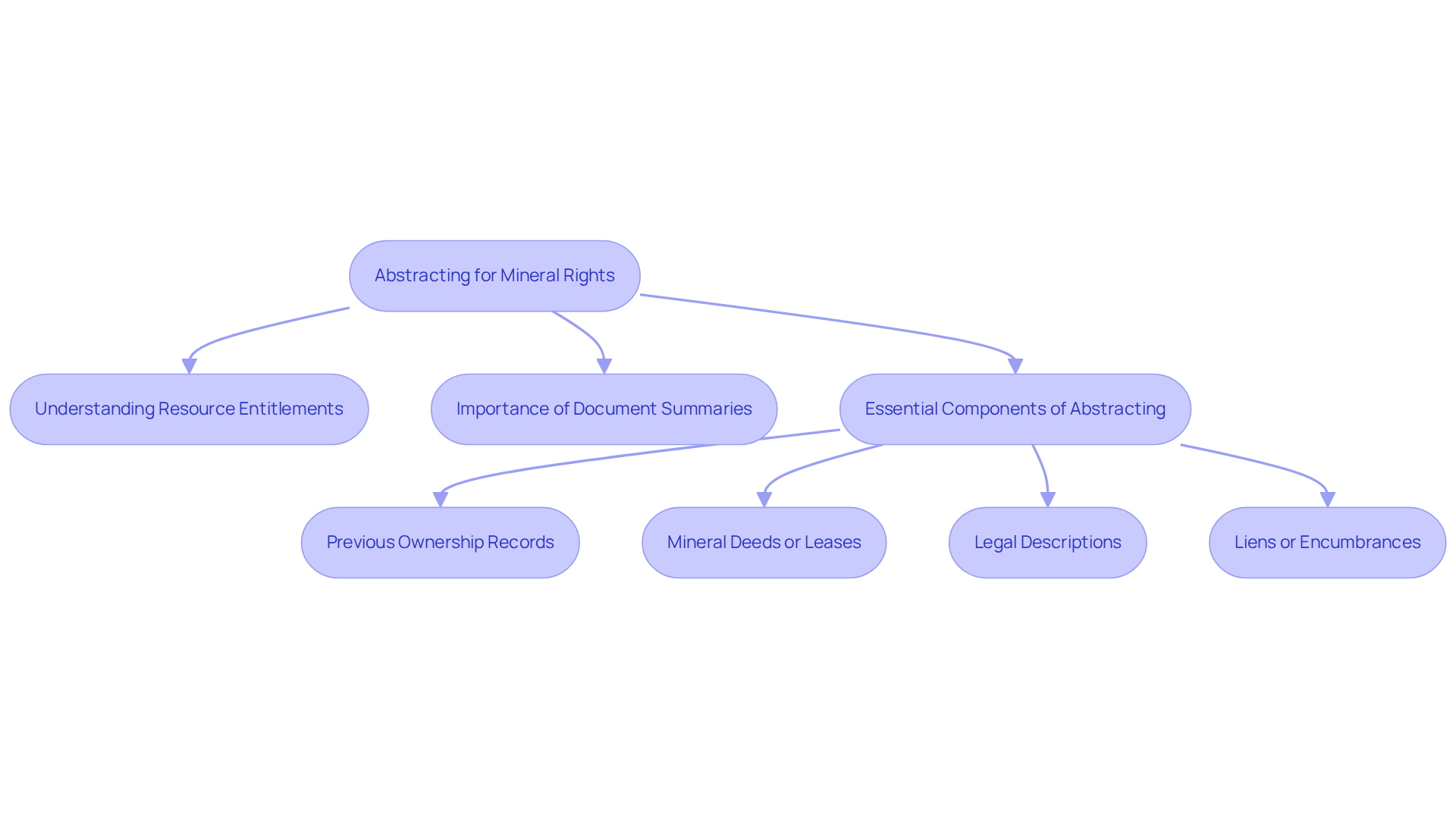
Understand the Basics of Abstracting for Mineral Rights
The process includes an overview of abstracting for mineral rights, which involves a comprehensive examination of a property's legal background, focusing on the possession and transfer of resource entitlements. This critical process encompasses several key aspects:
-
Understanding Resource Entitlements: Resource entitlements refer to the legal ownership of subsurface assets such as oil, gas, and minerals. These entitlements may exist independently from surface entitlements, meaning one party can own the land while another possesses the resources beneath it. Notably, a significant percentage of properties feature distinct resource entitlements, underscoring the importance of clarity in these transactions.
-
Importance of Document Summaries: A document summary serves as a record detailing the history of ownership and any transactions associated with the property. This summary is vital for verifying resource entitlements and ensuring the absence of conflicts regarding possession. An overview of abstracting for mineral rights is essential for establishing control over resource entitlements; it aids in early identification of potential issues and provides legal security for both existing owners and prospective buyers.
-
Essential Components of Abstracting: The abstracting process must include:
- Previous ownership records
- Any mineral deeds or leases
- Legal descriptions of the property
- Any liens or encumbrances affecting mineral rights
The review process for mineral rights typically entails examining title abstracts to establish a clear chain of title, documenting all transactions related to the property. As emphasized by industry experts, a thorough understanding of these elements is crucial for anyone involved in the management or transfer of resource entitlements. This foundational knowledge prepares you for the subsequent stages in creating an abstract for resource entitlements.
Follow the Step-by-Step Process for Creating an Abstract
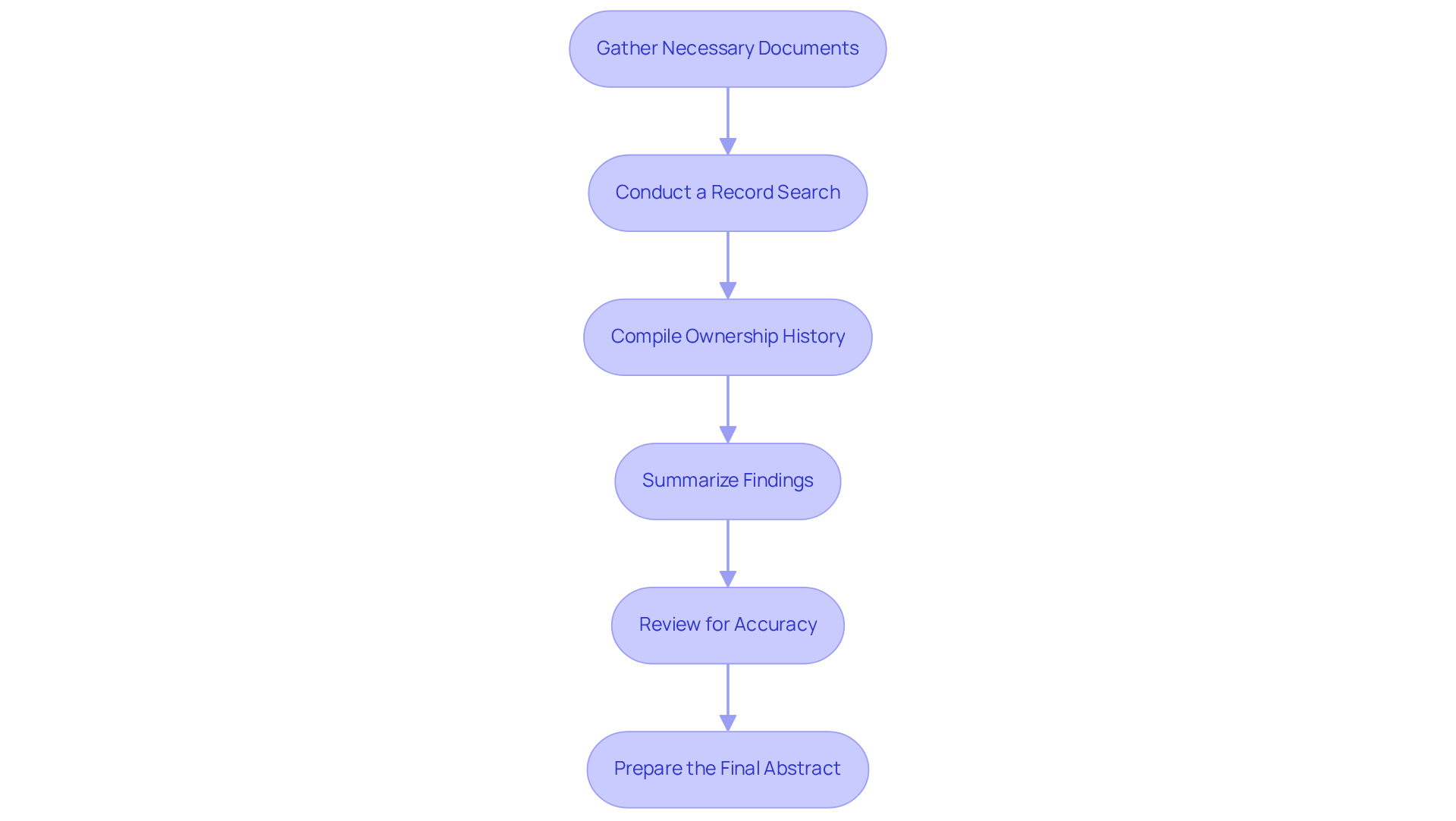
Creating an abstract for mineral rights involves several key steps:
-
Gather Necessary Documents: Start by collecting all relevant documents, including previous title abstracts, mineral deeds, lease agreements, and any court documents related to ownership disputes.
-
Conduct a Record Search: Execute a comprehensive record search to track the history of possession. This may involve visiting local courthouses or land offices and accessing online databases that provide property records.
-
Compile Ownership History: Document the chain of title, noting each transfer of ownership, the dates of transactions, and the parties involved in each transaction.
-
Summarize Findings: Create an overview of abstracting for mineral rights that includes a clear legal description of the property, any mineral rights associated with the property, and notable encumbrances or liens.
-
Review for Accuracy: Double-check all information for accuracy and completeness. Ensure that all documents are correctly referenced and that there are no gaps in the ownership history.
-
Prepare the Final Abstract: Format the abstract in a clear and professional manner, ensuring it is easy to read and understand. Include a title page, a table of contents, and the compiled ownership history and summary.
Adhering to these procedures will assist in guaranteeing that your overview of abstracting for mineral rights is both comprehensive and precise, providing a strong basis for any resource ownership transactions.
Identify and Troubleshoot Common Issues in Abstracting
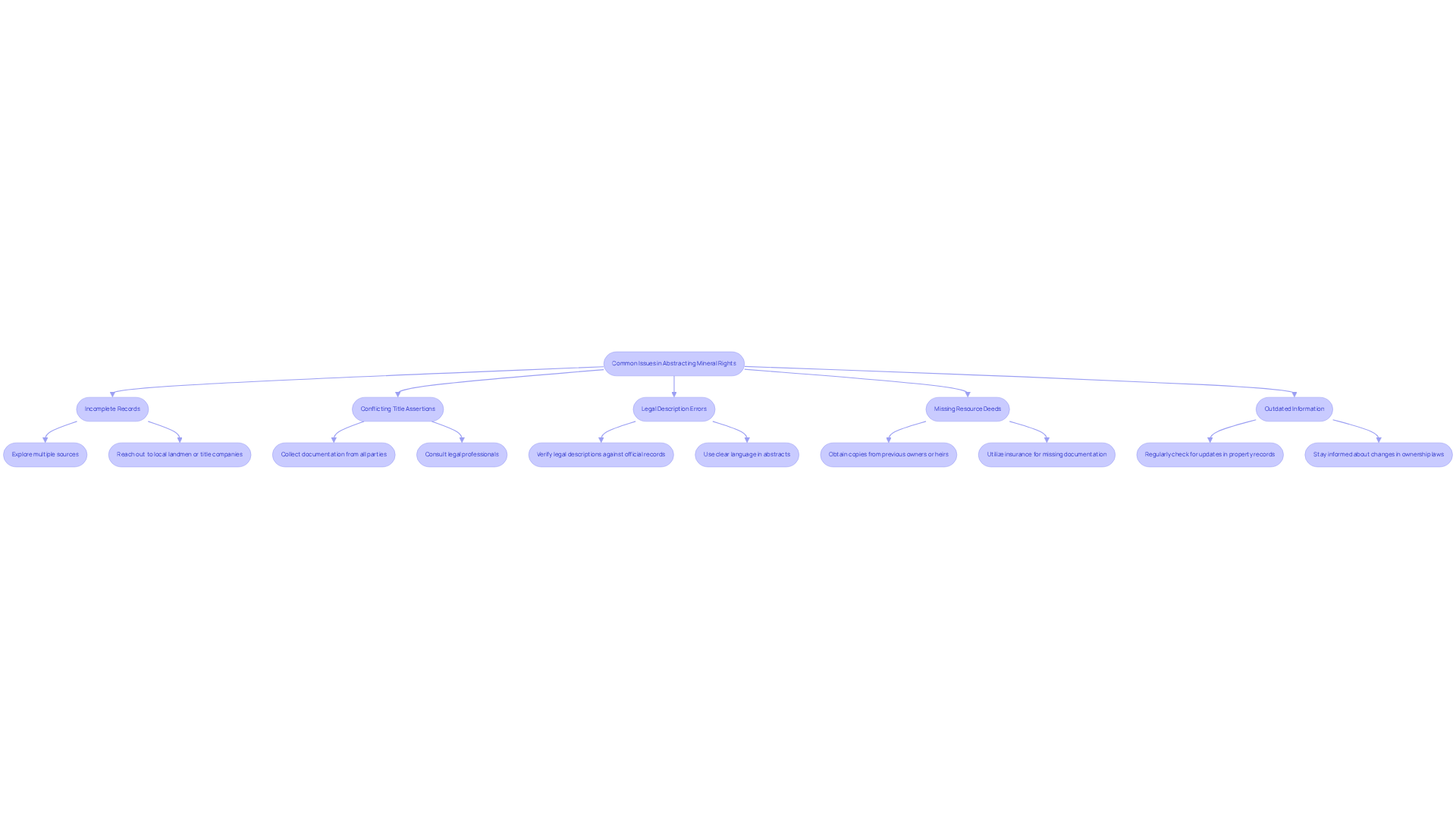
When conducting an overview of abstracting for mineral rights, several common issues may arise. Identifying and troubleshooting them effectively is crucial for ensuring accurate title research.
-
Incomplete Records: Historical records can sometimes be missing or incomplete. Statistics indicate that a significant portion of resource ownership searches encounters incomplete records, underscoring the necessity for detailed examination. To tackle this, explore multiple sources, including local courthouses, state archives, and online databases. Furthermore, reach out to local landmen or title companies for additional assistance.
-
Conflicting Title Assertions: Discrepancies in property rights often arise when multiple parties claim entitlements to the same resources. To resolve this, collect all relevant documentation from each party involved. In addition, consult legal professionals to clarify ownership based on the gathered evidence.
-
Legal Description Errors: Mistakes in legal descriptions can lead to significant complications. To prevent these issues, verify all legal descriptions against official records meticulously. Use clear and precise language when drafting your abstract to avoid ambiguity.
-
Missing Resource Deeds: The absence of resource deeds can complicate the verification process. To mitigate this, investigate the possibility of obtaining copies from previous owners or their heirs. Consider utilizing insurance to protect against potential claims arising from missing documentation.
-
Outdated Information: Ensuring that all information is current is crucial. To achieve this, regularly check for updates in property records to maintain accuracy. Stay informed about any changes in resource ownership laws, including the implications of the Marketable Record Title Act (MRTA), which streamlines ownership examination and addresses historical defects.
By proactively identifying and addressing these common issues, you can significantly enhance the accuracy and reliability outlined in the overview of abstracting for mineral rights. This ultimately leads to more efficient title research.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of abstracting for mineral rights is essential for anyone involved in the management or transfer of resource entitlements. This process not only clarifies ownership but also provides a legal framework that safeguards transactions related to subsurface assets. By grasping key concepts such as resource entitlements, document summaries, and essential components, stakeholders can navigate the complexities of mineral rights with confidence.
The article outlines a systematic approach to creating an abstract, emphasizing the importance of thorough documentation and accurate record-keeping. From gathering necessary documents to identifying and troubleshooting common issues, each step is crucial for establishing a clear chain of title. Furthermore, addressing potential challenges, such as incomplete records and conflicting title assertions, ensures that the abstract is both reliable and comprehensive.
Ultimately, the significance of abstracting for mineral rights extends beyond mere documentation; it represents a foundational element in securing ownership and facilitating transactions in the resource sector. By applying the insights and best practices discussed, individuals can enhance their understanding and execution of mineral rights abstracting, thereby contributing to more efficient and secure property transactions. Taking proactive steps in this process not only mitigates risks but also empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions in the realm of mineral rights.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the process of abstracting for mineral rights?
Abstracting for mineral rights involves a comprehensive examination of a property's legal background, focusing on the possession and transfer of resource entitlements.
What are resource entitlements?
Resource entitlements refer to the legal ownership of subsurface assets such as oil, gas, and minerals, which can exist independently from surface entitlements.
Why is it important to understand the distinction between surface and resource entitlements?
Understanding the distinction is important because one party can own the land while another possesses the resources beneath it, and many properties have separate resource entitlements.
What is the role of a document summary in the abstracting process?
A document summary records the history of ownership and transactions associated with the property, verifying resource entitlements and ensuring the absence of conflicts regarding possession.
What are the essential components of the abstracting process?
Essential components include previous ownership records, any mineral deeds or leases, legal descriptions of the property, and any liens or encumbrances affecting mineral rights.
What does the review process for mineral rights entail?
The review process typically involves examining title abstracts to establish a clear chain of title and documenting all transactions related to the property.
Why is a thorough understanding of abstracting important?
A thorough understanding is crucial for anyone involved in the management or transfer of resource entitlements, as it prepares them for subsequent stages in creating an abstract for resource entitlements.




