Overview
The article emphasizes the effective utilization of property tax history search tools for precise title research. It underscores the significance of leveraging various resources, including:
- county tax assessor websites
- state tax databases
- local government portals
to compile essential tax information. Furthermore, it addresses the common challenges encountered in title research and proposes strategies to overcome these obstacles, ultimately enhancing both accuracy and efficiency.
Introduction
In the intricate world of real estate, understanding property tax history transcends routine tasks; it is a crucial component that significantly influences title research outcomes. Mastering the diverse array of property tax history search tools available allows professionals to unlock a wealth of information, ensuring accuracy and compliance in their findings.
However, the ever-evolving landscape of property tax laws, coupled with the complexities of data interpretation, presents challenges. How can researchers effectively navigate these obstacles to enhance their efficiency and reliability? This question underscores the importance of strategic approaches in the realm of property tax research.
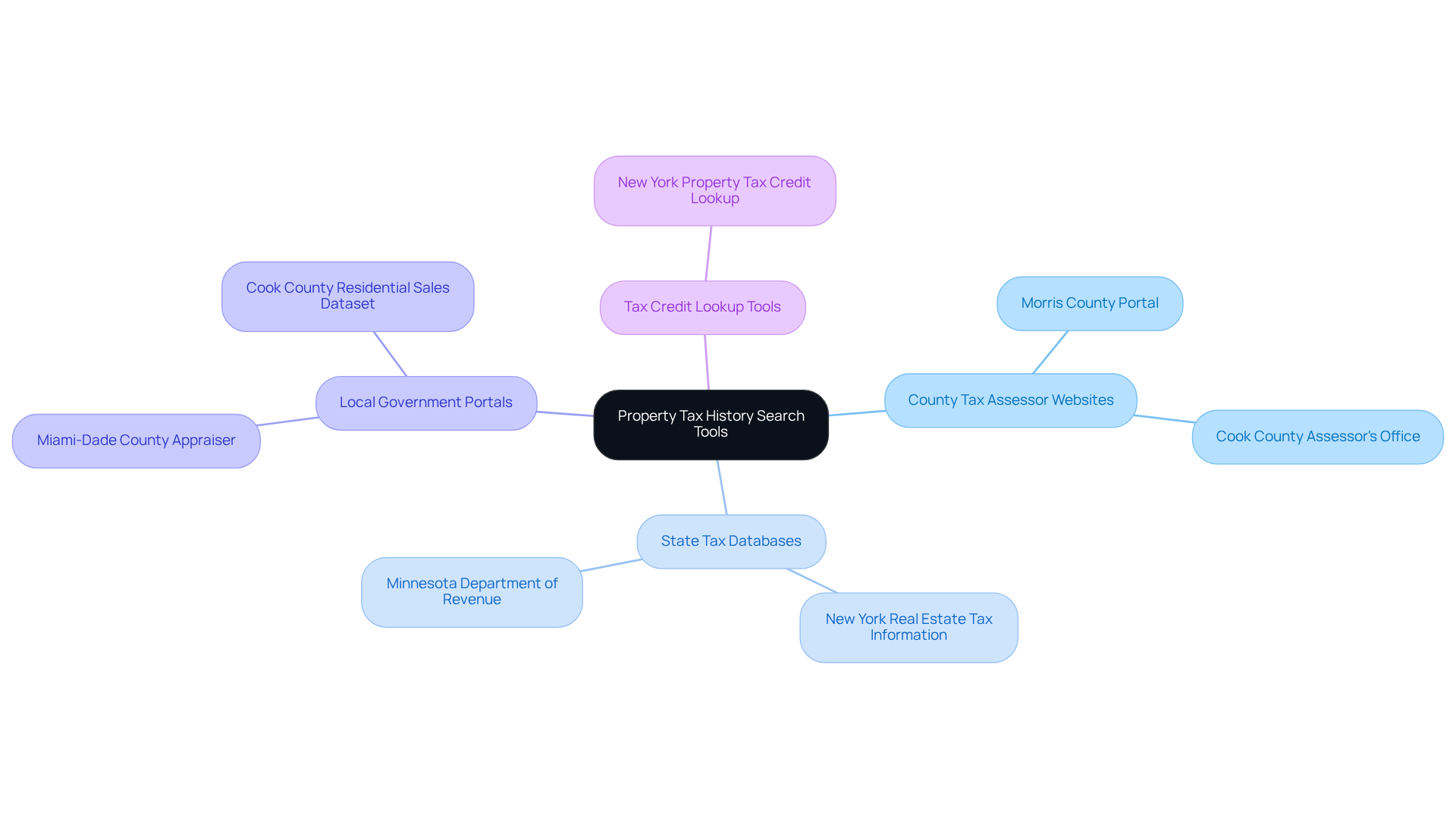
Understand Property Tax History Search Tools
To effectively conduct tax history searches, it is essential to utilize along with a range of online databases. Here are some vital resources:
- County Tax Assessor Websites: These platforms are crucial for accessing real estate tax records. Approximately 70% of research professionals rely on these websites, as they provide direct access to local tax data. For instance, Morris County's tax records can be accessed through their dedicated portal.
- State Tax Databases: Many states maintain centralized records that compile tax details, streamlining the research process. New York's real estate tax information exemplifies such a resource, offering comprehensive data for title researchers. Additionally, the Minnesota Department of Revenue provides tax data from 2005 to 2024, invaluable for historical research.
- Local Government Portals: Websites like the Miami-Dade County Appraiser offer extensive tools for real estate searches, including tax evaluations and exemptions. These local portals are indispensable for quickly acquiring detailed real estate information. Furthermore, Cook County, Illinois, maintains a dataset of residential sales that assists in real estate analysis.
- Tax Credit Lookup Tools: These tools are fundamental for identifying applicable tax credits, which can significantly impact the financial obligations associated with a real estate asset. For example, New York provides a Property Tax Credit Lookup tool that facilitates this process.
By leveraging these resources, title researchers can efficiently gather essential details about tax history with the help of property tax history search tools, ensuring accuracy in their title research efforts. The integration of machine learning and optical character recognition technologies, as demonstrated by innovative platforms like Parse AI, further enhances the speed and accuracy of this research. Consequently, professionals can complete abstracts and reports more effectively. Case studies indicate that Parse AI's approach has resulted in significant cost savings and improved efficiency for real estate professionals.
Utilize Search Tools for Property Tax History
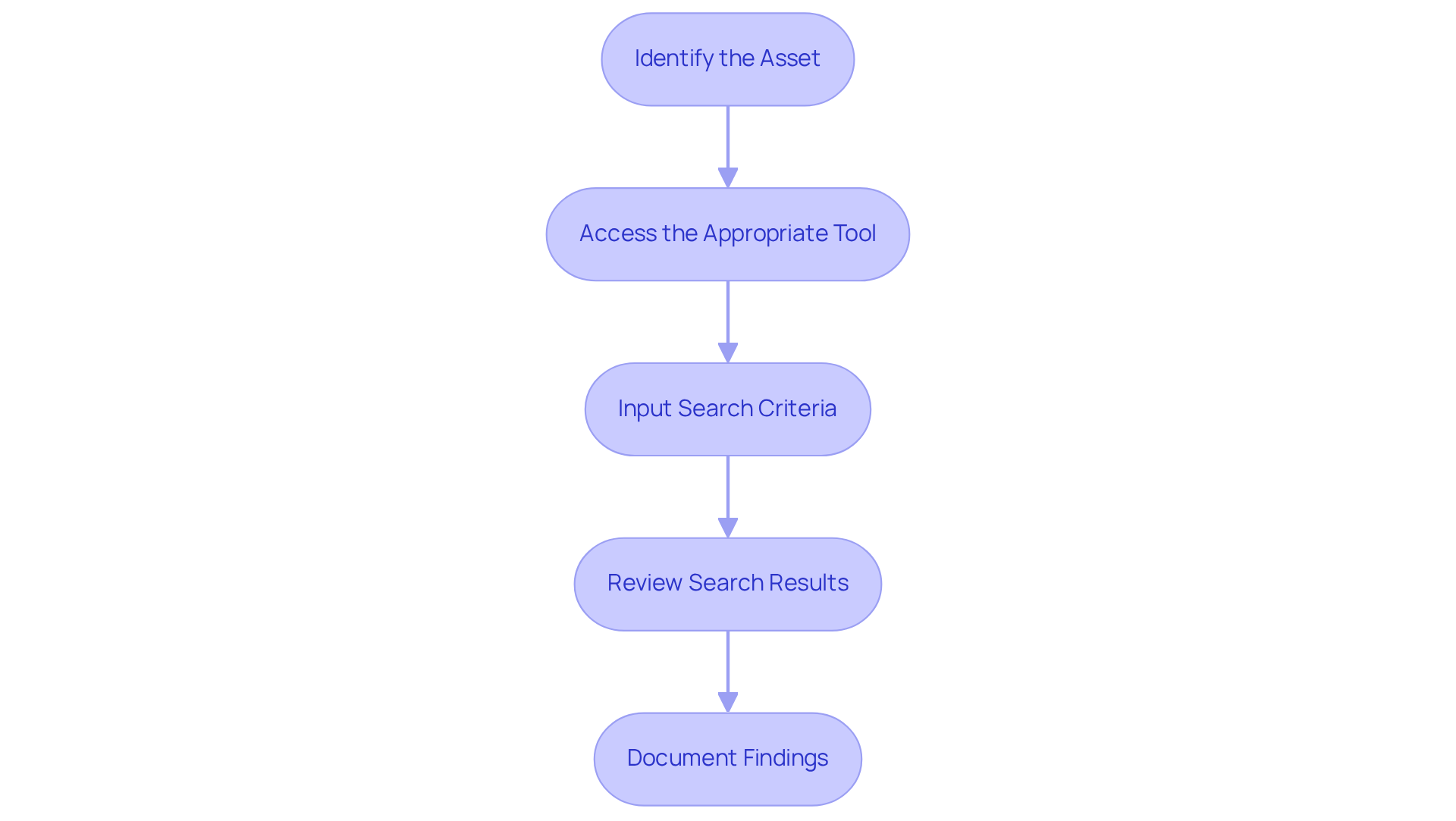
To utilize property tax history search tools effectively, follow these steps:
- Identify the Asset: Collect vital details about the asset, including the address, parcel number, or owner’s name. This information is necessary for conducting searches.
- Access the Appropriate Tool: Navigate to the relevant county or state tax assessor's website. For instance, if you are investigating real estate in Passaic County, you can access their page.
- Input Search Criteria: Enter the required fields, such as the location address or tax year. Ensure that you fill in all mandatory fields marked with an asterisk (*) to retrieve accurate results.
- Review Search Results: Analyze the search results carefully. Look for essential details such as , payment history, and any outstanding liens. For example, the page offers comprehensive details, including tax bills and exemptions.
- Document Findings: Keep a record of your findings, including screenshots or notes on important details. This documentation will be invaluable for your research and any subsequent transactions.
By following these steps, you can effectively use property tax history search tools to collect the essential details for precise research.
Overcome Challenges in Title Research
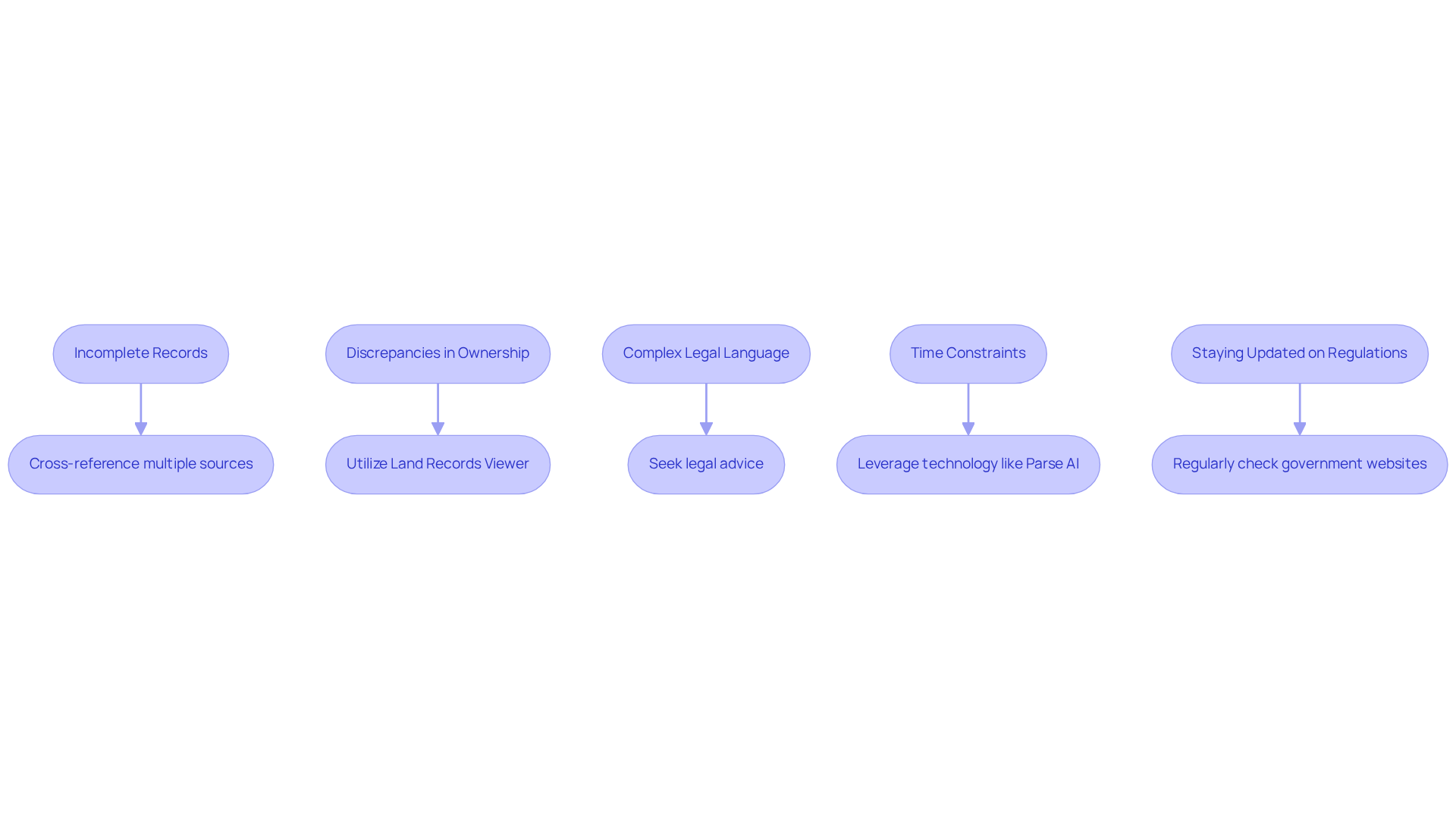
Title research presents various challenges that can hinder the accuracy and efficiency of the process. Understanding these challenges is crucial for , as it lays the groundwork for successful outcomes. Here are some common challenges and strategies to overcome them:
- Incomplete or Inconsistent Records: Property records may be incomplete or contain discrepancies. To address this issue, cross-reference multiple sources, such as county tax records and local government databases, to verify information. According to industry insights, there are 16 frequent public records mistakes that researchers should be aware of to enhance their accuracy.
- Discrepancies in Ownership Information: Ownership records may not always align due to changes in asset ownership or errors in documentation. Utilize tools like the to access comprehensive ownership history and resolve discrepancies. As noted by industry leaders, proactive measures are essential in effectively addressing these discrepancies.
- Complex Legal Language: Legal documents can be challenging to interpret. Consider seeking advice from a legal specialist or using resources that clarify common legal terms and expressions associated with property ownership. Continuous education for land professionals builds confidence in their capabilities.
- Time Constraints: Title researchers often face tight deadlines. To enhance efficiency, leverage technology like Parse AI, which employs machine learning to quickly extract pertinent information from document titles, enabling faster completion of abstracts and reports. This technology is particularly crucial as the property company sector navigates anticipated market fluctuations impacting transaction volumes and revenue in 2025.
- Staying Updated on Regulations: Property tax laws and regulations can change frequently. Regularly check state and local government websites for updates on property tax laws, utilizing property tax history search tools to ensure compliance requirements are met. Staying compliant is vital as the regulatory environment continues to evolve.
By proactively addressing these challenges, title researchers can enhance their workflow and ensure accurate and compliant title research, thereby minimizing the risk of errors that could lead to legal disputes or financial losses.
Conclusion
Mastering property tax history search tools is crucial for anyone involved in title research. These tools not only streamline the process but also guarantee that the information gathered is accurate and reliable. By leveraging various resources such as county tax assessor websites, state tax databases, and local government portals, title researchers can adeptly navigate the complexities of property tax records.
Throughout this article, key strategies for utilizing these search tools have been discussed, including:
- Identifying assets
- Accessing appropriate platforms
- Documenting findings
Furthermore, the challenges faced in title research—such as incomplete records and discrepancies in ownership information—have been highlighted alongside practical solutions. Emphasizing the role of technology, particularly machine learning applications like Parse AI, illustrates how innovation can enhance efficiency and accuracy in this critical field.
Ultimately, understanding and effectively employing property tax history search tools is vital for successful title research. By staying informed about best practices and overcoming common challenges, researchers can significantly reduce the risk of errors that may lead to legal complications or financial setbacks. As the landscape of property transactions continues to evolve, embracing these tools and strategies will not only improve research outcomes but also bolster confidence in the integrity of property ownership records.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are property tax history search tools?
Property tax history search tools are resources used to conduct searches for real estate tax records, helping researchers gather essential details about tax history.
Why are county tax assessor websites important?
County tax assessor websites provide direct access to local tax data and are used by approximately 70% of research professionals for accessing real estate tax records.
How do state tax databases assist in property tax research?
State tax databases maintain centralized records that compile tax details, streamlining the research process. For example, New York's real estate tax information offers comprehensive data for title researchers.
What information can local government portals provide?
Local government portals offer extensive tools for real estate searches, including tax evaluations, exemptions, and datasets of residential sales that assist in real estate analysis.
What are tax credit lookup tools?
Tax credit lookup tools help identify applicable tax credits that can significantly impact the financial obligations associated with a real estate asset, such as the Property Tax Credit Lookup tool provided by New York.
How do advanced technologies like machine learning enhance property tax research?
Technologies like machine learning and optical character recognition improve the speed and accuracy of property tax research, allowing professionals to complete abstracts and reports more effectively.
What benefits have been observed from using innovative platforms like Parse AI?
Case studies indicate that platforms like Parse AI have resulted in significant cost savings and improved efficiency for real estate professionals in their research efforts.




