Overview
This article provides a comprehensive comparison of various GIS platforms tailored for mineral rights management, meticulously assessing their features, advantages, and drawbacks to assist professionals in identifying the most suitable option. It underscores the critical importance of considerations such as budget constraints, user experience, and specific operational requirements. Real-world examples and industry insights are presented to illustrate how the appropriate GIS platform can significantly enhance resource management and operational efficiency.
Introduction
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have fundamentally transformed the management of mineral rights, providing exceptional tools for visualizing and analyzing spatial data pertinent to land ownership and resource availability. As industry professionals increasingly depend on GIS platforms to refine decision-making and optimize operations, it is crucial to grasp the intricacies of these technologies.
Yet, with an abundance of options available, how can one ascertain which GIS solution aligns best with their specific requirements and budget constraints? This article explores the features, advantages, and challenges of leading GIS platforms for mineral rights management, equipping readers with the insights essential for making informed decisions in this vital sector.
Understanding GIS Platforms in Mineral Rights Management
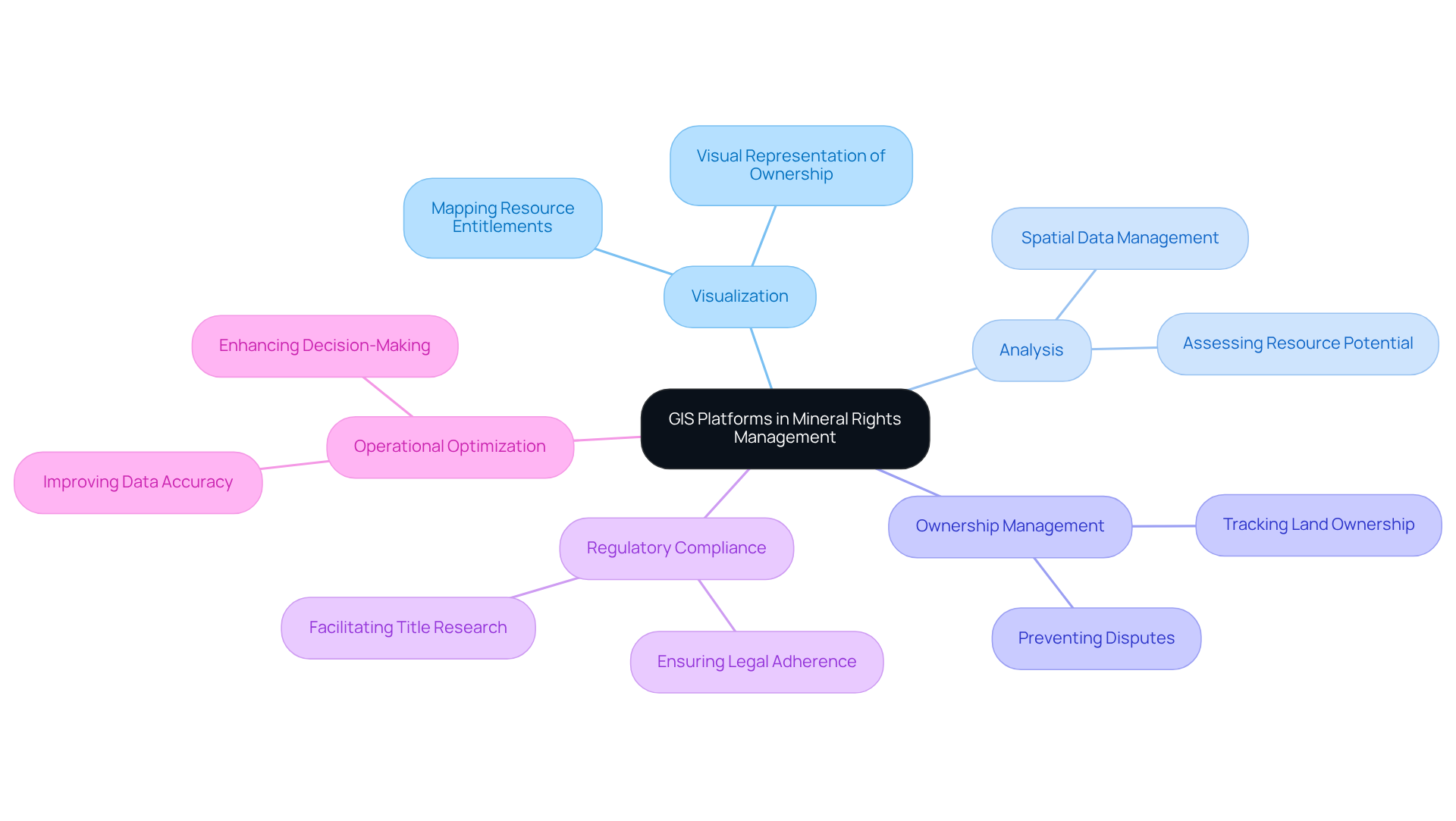
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) serve as powerful tools for managing spatial data, especially when utilizing GIS platforms for mineral rights management. These GIS platforms for mineral rights management empower users to visualize, analyze, and interpret data related to land ownership, resource deposits, and regulatory compliance. In the context of resource oversight, GIS platforms for mineral rights management enable land professionals and resource owners to effectively monitor ownership boundaries, assess resource potential, and manage leases. The integration of GIS platforms for mineral rights management into resource management not only enhances data accuracy but also improves decision-making processes, thereby solidifying their role as a critical asset for industry experts.
The use of GIS platforms for mineral rights management in this domain facilitates the mapping of resource entitlements, providing a visual representation of ownership and potential resource availability. This functionality is vital for preventing disputes and ensuring adherence to legal requirements, particularly for title research directors who navigate intricate legal frameworks. Recent advancements in GIS technology, exemplified by the Bureau of Land Management and the USGS's launch of a hub for streamlined visualization and access to Sagebrush Geospatial Data, have significantly improved land ownership tracking, enabling more precise evaluations and strategic planning.
Industry leaders underscore the importance of GIS platforms for mineral rights management in tracking land ownership, emphasizing that their application can optimize operations and enhance compliance. For instance, the U.S. Geological Survey's initiatives in developing essential resource lists underscore the criticality of accurate geospatial data in effectively managing resource assets. As GIS technology continues to evolve, its relevance in resource ownership oversight is poised to grow, especially through the use of GIS platforms for mineral rights management, equipping professionals with the necessary tools to make informed decisions and enhance resource utilization. Furthermore, the involvement of Mineral Management Companies (MMCs) in navigating the complexities of resource entitlements, including legal compliance and negotiations, exemplifies the collaborative nature of successful oversight.
Key Features of Leading GIS Platforms
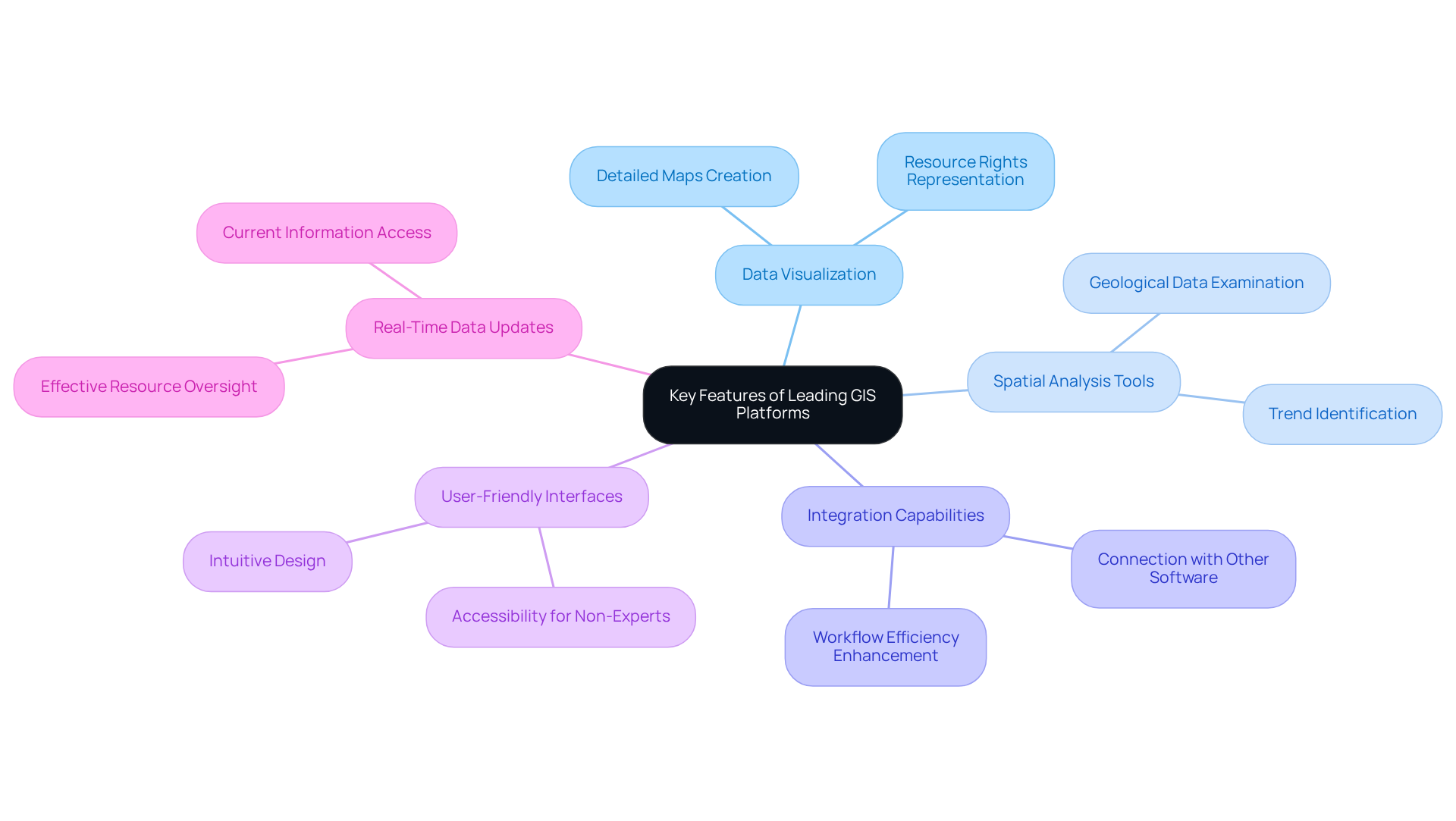
Prominent GIS platforms for mineral rights management, including Esri ArcGIS, QGIS, and Landdox, are equipped with essential features that cater specifically to the needs of land management professionals. These features are pivotal for effective decision-making and operational success.
- Data Visualization: These platforms facilitate the creation of detailed maps that effectively represent resource rights and ownership boundaries, thereby enhancing decision-making processes.
- Spatial Analysis Tools: Users can leverage advanced tools to examine geological data, evaluate resource potential, and identify trends. This capability significantly improves strategic planning efforts.
- Integration Capabilities: The ability to seamlessly connect with other software systems, including title research databases and land administration tools, greatly enhances workflow efficiency.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Designed for accessibility, these intuitive interfaces accommodate professionals who may lack extensive technical expertise, ensuring ease of use.
- Real-Time Data Updates: Features that support dynamic data updates ensure users have access to the most current information, which is crucial for effective resource oversight.
Collectively, these features empower experts to manage resource ownership more efficiently, underscoring the importance of selecting the appropriate GIS platforms for mineral rights management to achieve maximum operational effectiveness.
Evaluating Pros and Cons of Each GIS Solution
When evaluating GIS platforms for mineral rights management, it is crucial to analyze the strengths and weaknesses of each solution to make informed decisions.
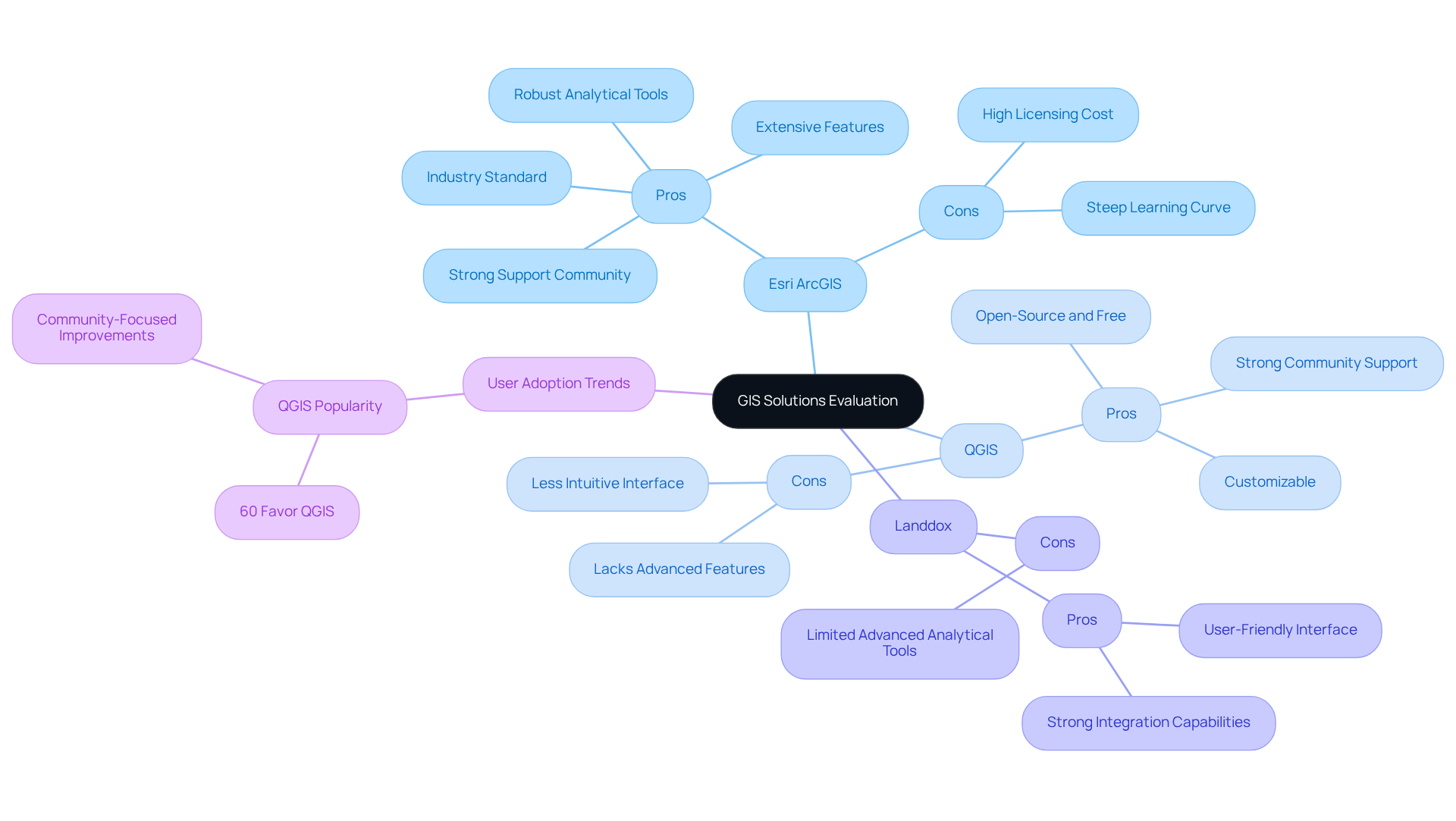
Esri ArcGIS
Pros: As the industry standard, ArcGIS offers extensive features, a strong support community, and robust analytical tools that cater to complex land management needs. Its capabilities are well-documented, making it a reliable choice for professionals.
Cons: However, the high cost associated with licensing and the steep learning curve for new users can be significant barriers, particularly for smaller organizations or those with limited budgets.
QGIS
Pros: QGIS stands out as an open-source alternative that is free to use, making it highly accessible for land management professionals. Its customizable nature allows users to tailor the platform to their specific needs, and it benefits from a strong community that provides support and resources.
Cons: Despite its advantages, QGIS may lack some advanced features found in proprietary software, and its user interface can be less intuitive, which may pose challenges for new users.
Landdox
Pros: Designed specifically for land management, Landdox offers a user-friendly interface and strong integration capabilities with existing systems, making it an attractive option for organizations focused on land rights.
Cons: However, it is limited in advanced analytical tools compared to more established platforms like ArcGIS, which may restrict its utility for more complex analyses.
Regarding user adoption rates, QGIS has experienced a notable rise in popularity among land professionals due to its cost-effectiveness and flexibility. A recent survey revealed that more than 60% of users in the resource management sector favor QGIS for its flexibility and community-focused improvements. This statistic is supported by insights from industry experts such as James Graham, who noted the growing trend of QGIS adoption in the field. Furthermore, case studies from organizations like INDOT and VTrans illustrate the practical applications of these GIS platforms, showcasing their effectiveness in real-world scenarios. By weighing these pros and cons, professionals can better assess which GIS platforms for mineral rights management align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Determining the Right GIS Platform for Your Needs
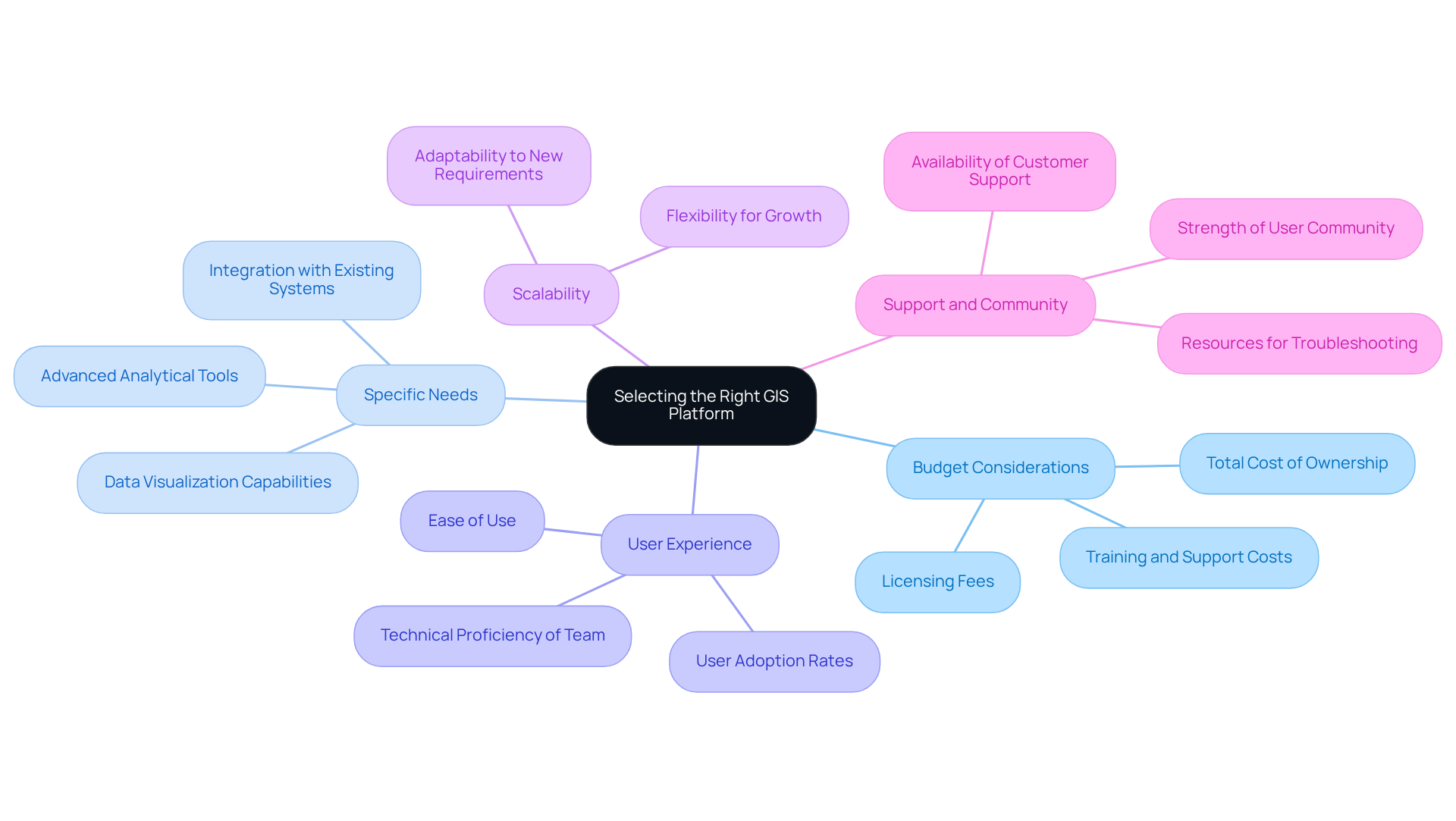
Selecting the appropriate GIS platforms for mineral rights management necessitates a thorough evaluation of several essential factors.
-
Budget Considerations: Assessing the total cost of ownership is crucial. This encompasses not only licensing fees but also training and ongoing support. Industry leaders emphasize that understanding the full financial commitment can prevent unexpected expenses down the line. A senior land consultant highlights the significance of budget planning: "Investing in the appropriate GIS platforms for mineral rights management upfront can save substantial costs in the long run."
-
Specific Needs: Clearly defining the features vital for your operations is imperative. This may include capabilities for data visualization, integration with existing systems, or advanced analytical tools tailored to your workflow.
-
User Experience: The technical proficiency of your team plays a significant role in platform selection. Statistics indicate that over 70% of professionals prioritize ease of use in their decision-making process. Opting for a solution that aligns with their skill levels ensures smooth adoption and effective utilization.
-
Scalability: Choose a platform capable of evolving with your organization. As operational demands change, the GIS solution should be flexible enough to accommodate growth and new requirements.
-
Support and Community: Investigate the availability of customer support and the strength of the user community. A robust support system and an engaged user base provide invaluable resources for troubleshooting and sharing best practices.
Real-world examples illustrate that organizations investing in user-friendly GIS solutions often experience significant enhancements in operational efficiency and data handling. By meticulously evaluating these factors, professionals can make informed decisions that enhance their processes using GIS platforms for mineral rights management, ultimately leading to improved outcomes and cost savings.
Conclusion
The exploration of GIS platforms for mineral rights management underscores their vital role in enhancing spatial data handling and decision-making processes within the industry. By leveraging these technologies, professionals can visualize land ownership effectively, assess resource potential, and ensure compliance with regulatory frameworks, ultimately driving operational success.
Key insights from the article emphasize the necessity of selecting the appropriate GIS platform based on features such as:
- Data visualization
- Spatial analysis tools
- User-friendliness
Each platform—be it Esri ArcGIS, QGIS, or Landdox—presents distinct advantages and limitations that must be carefully considered against organizational needs and budget constraints. Evaluating these factors not only optimizes resource management but also fosters collaboration among stakeholders involved in mineral rights oversight.
Ultimately, integrating GIS technology into mineral rights management transcends mere operational enhancement; it is a strategic imperative. As the industry evolves, embracing the right GIS solutions can lead to improved efficiency, reduced disputes, and better resource utilization. Professionals are urged to adopt a proactive approach in evaluating and implementing these platforms to navigate the complexities of mineral rights management effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of GIS platforms in mineral rights management?
GIS platforms serve as powerful tools for managing spatial data, allowing users to visualize, analyze, and interpret data related to land ownership, resource deposits, and regulatory compliance in mineral rights management.
How do GIS platforms enhance decision-making in resource management?
By improving data accuracy and providing visual representations of ownership and resource availability, GIS platforms enhance decision-making processes for land professionals and resource owners.
What specific functions do GIS platforms provide for land professionals?
GIS platforms enable land professionals to monitor ownership boundaries, assess resource potential, manage leases, and prevent disputes, ensuring adherence to legal requirements.
What recent advancements have been made in GIS technology for mineral rights management?
Recent advancements include the Bureau of Land Management and the USGS's launch of a hub for streamlined visualization and access to Sagebrush Geospatial Data, which significantly improves land ownership tracking.
Why is accurate geospatial data critical in managing resource assets?
Accurate geospatial data is essential for effective resource management, as it facilitates the mapping of resource entitlements and supports compliance with legal frameworks.
How do industry leaders view the importance of GIS platforms in tracking land ownership?
Industry leaders emphasize that GIS platforms optimize operations and enhance compliance, making them critical assets for tracking land ownership and managing resources.
What is the role of Mineral Management Companies (MMCs) in resource entitlement oversight?
MMCs navigate the complexities of resource entitlements, including legal compliance and negotiations, highlighting the collaborative nature of successful resource management.




