Introduction
Understanding the intricacies of property liens is essential for anyone involved in real estate transactions, from homeowners to industry professionals. A lien on a house represents a legal claim by a lender or creditor, which can significantly impact property ownership and sales. This article explores the fundamentals of liens, including their origins, types, and the implications they carry.
It delves into the process by which loan companies place liens on properties and examines the different categories such as mortgage, tax, judgment, and mechanic’s liens. The discussion extends to the impact of liens on selling a house, providing insights into potential financial and legal complications. Practical advice on removing liens and best practices for homeowners to prevent liens from arising is also covered.
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of these topics, individuals can navigate the real estate landscape more effectively, ensuring smoother transactions and safeguarding their financial interests.
What is a Lien on a House?
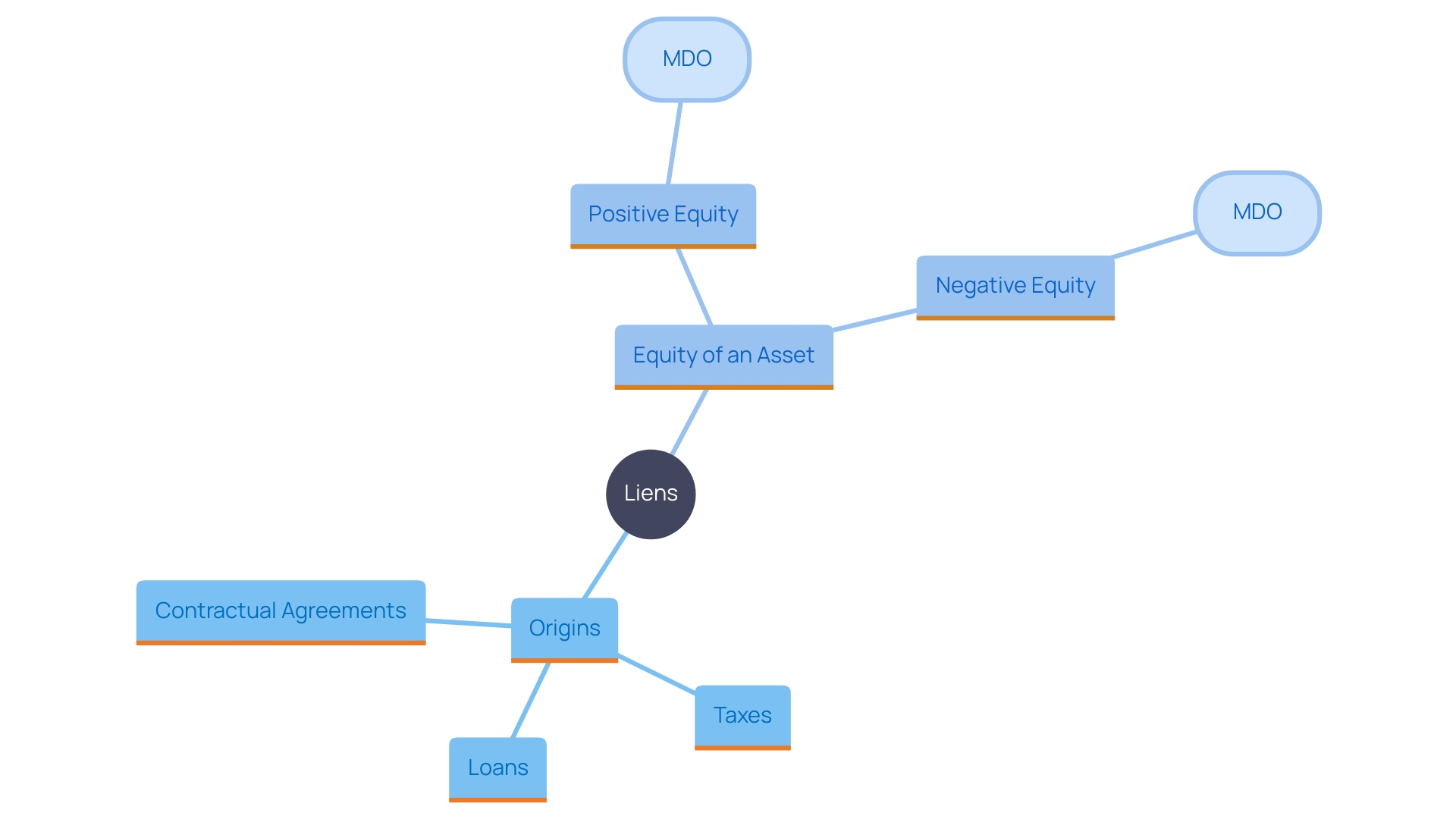
A signifies a or creditor to secure a debt or obligation. This claim grants the lienholder the authority to of the asset if the borrower defaults on their financial obligations. Liens can arise from different origins, such as loans, taxes, or contractual agreements, and they remain until the related debt is completely settled. The amount of equity connected to each asset is determined by comparing its estimated current value against the (MDO). Properties with an MDO exceeding their estimated value are in a negative equity position, while those with a higher estimated value than MDO are in a positive equity position. , comprising more than 50 million first- and second-mortgage claims, are utilized to derive this information, which is modified for amortization and home equity usage to reflect the accurate MDO for each asset.
How Does a Loan Company Put a Lien on a House?
When a loan organization offers funding for a house acquisition, it usually imposes a claim on the asset as security. This guarantees that the creditor has a legal right to the asset in the event of the borrower's failure to repay. The claim is documented in , making the financier's stake in the asset known to other possible creditors. The procedure of establishing a claim requires the borrower to consent to the loan conditions, including the creditor's authority to seize the asset if the loan is not repaid. This practice is a standard part of securing a home loan and plays a crucial role in protecting the . 'As per a recent report, the total equity owned by homeowners in the United States has attained a record high of $16.9 trillion, emphasizing the significant value that provide for creditors.'. Additionally, property claims are a frequent category of encumbrance that impacts . Adequate preparation and comprehension of loan responsibilities are crucial for both financiers and borrowers to guarantee a .
Types of Liens on a House
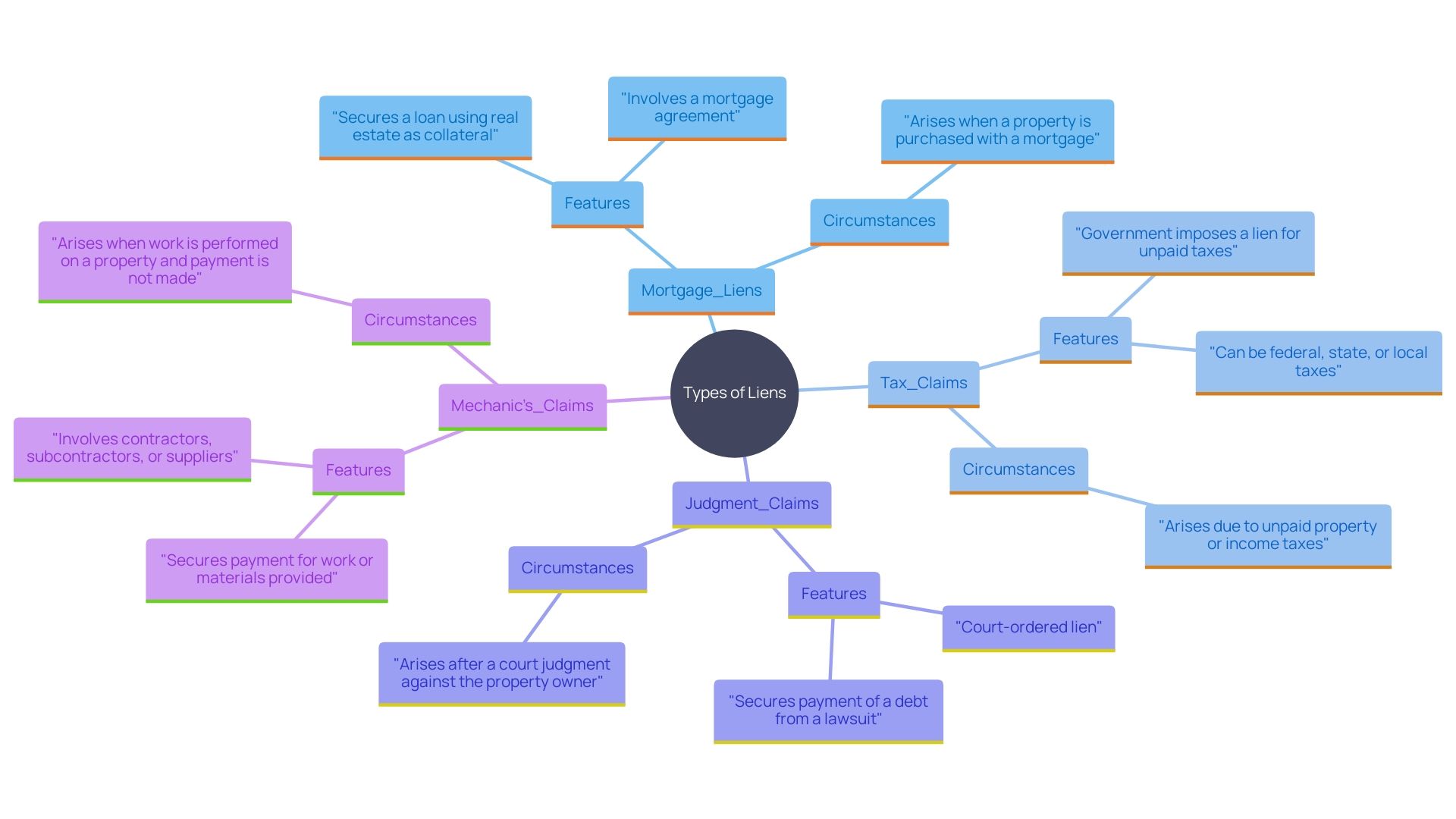
Liens can be categorized into various types based on their origin and nature. Each type of lien represents a claim on a property due to different circumstances:
- : These are created when a borrower takes out a mortgage to purchase a home. They are the most prevalent form of claim and are held by the lender until the mortgage is completely settled. '- Tax Claims: Imposed by governmental organizations for unpaid real estate taxes, tax claims can significantly influence real estate transactions.'. An asset with a tax claim cannot be sold or refinanced until the overdue taxes are settled.
- : Arising from court rulings against the asset owner for outstanding obligations, these claims can complicate ownership and transfer. They guarantee that creditors obtain payment from the proceeds of a real estate sale.
- : Submitted by contractors or suppliers who have not received payment for work done on the property, mechanic’s claims can be complex due to differing state regulations. For instance, modern rights laws generally require filing within a set number of days after the completion of the project, ensuring tradesmen are compensated.
Comprehending these claim types is essential for real estate experts. For example, an asset that recently underwent construction may still be subject to mechanic’s claims if the state’s claim rights timelines have not expired. Awareness of these timelines helps avoid unexpected financial liabilities and ensures a smoother transaction process.
Impact of a Lien on Selling a House
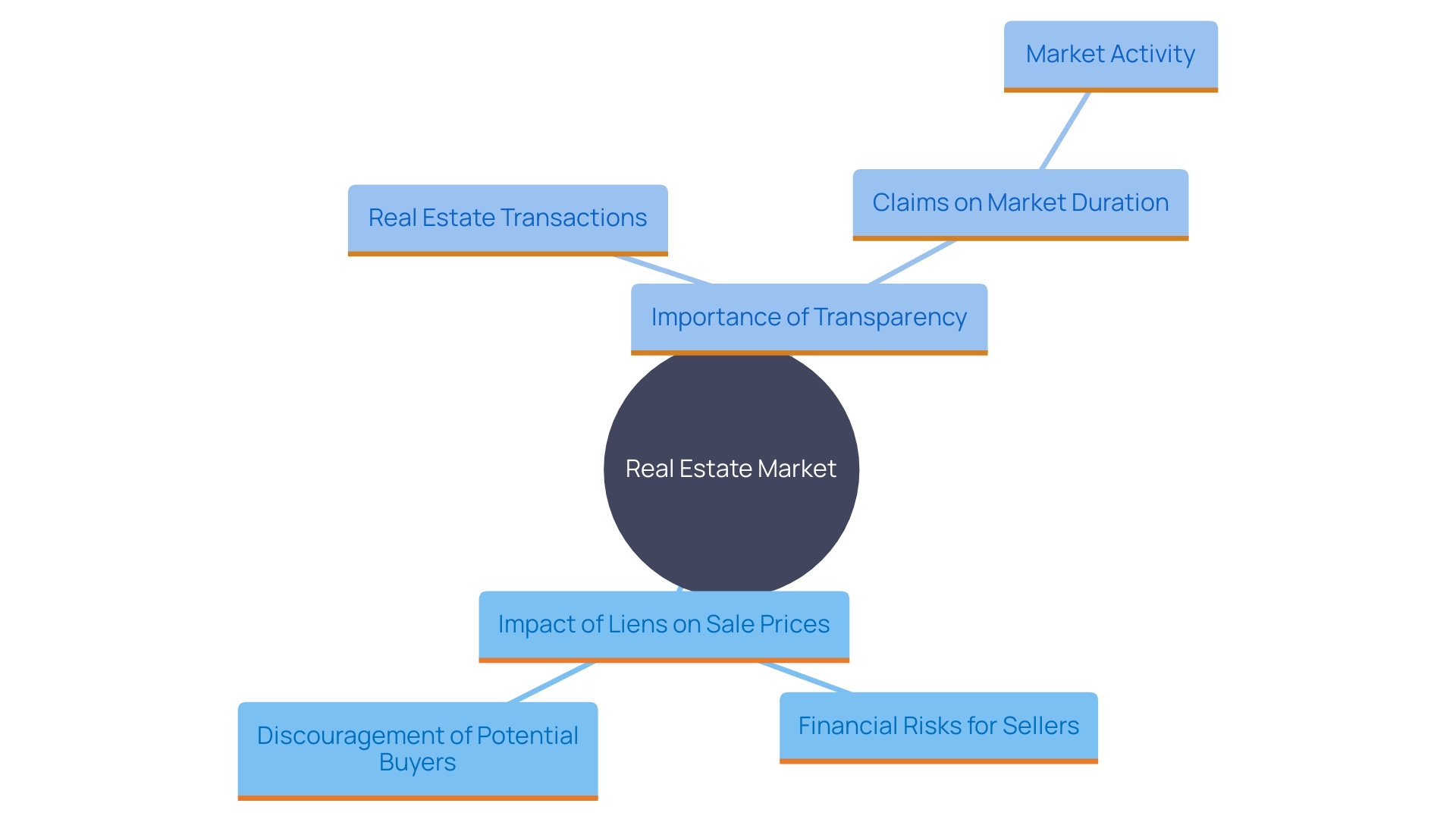
Liens on a real estate asset can severely impact the sale process, requiring resolution before the transfer to a new owner. Sellers must often resolve the debt linked to the claim during closing, potentially complicating their financial situation. For instance, a in London, Ontario, experienced a staggering drop in sale price from $738,400 to $435,000 within two years due to a lender taking possession because of unpaid mortgage payments. This case highlights the financial risks sellers encounter when claims are unresolved.
Possible purchasers might also be discouraged by properties with current claims, adding another layer of complexity to negotiations. As stated by the Real Estate Council of Ontario, brokers and sales agents are required to reveal important information, including , since they can greatly affect a buyer's choice. This requirement highlights the and thorough to avoid complications in the sale process.
Furthermore, the existence of claims can result in prolonged duration on the market, as cautious purchasers may negotiate more aggressively or withdraw completely. This was evident in a recent report showing the real estate market in Norfolk County holding steady, despite some fluctuations in property sales. The existence of claims and other title concerns can influence market activity and buyer trust, making it essential for sellers to tackle these matters swiftly to enable smoother transactions.
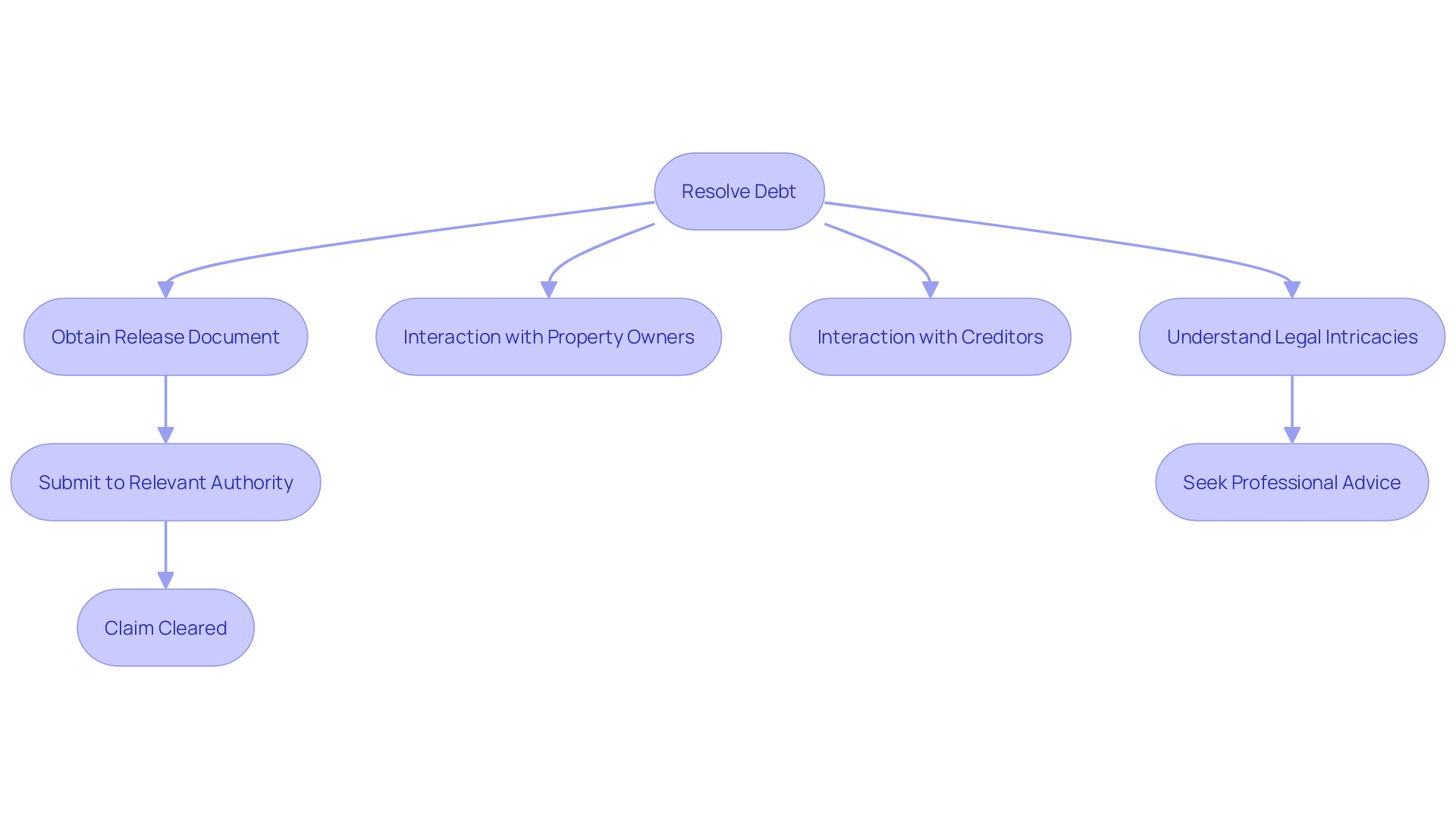
How to Remove a Lien from a House
Clearing a claim usually requires settling the obligation that resulted in its establishment. Resolution of the debt typically leads to the holder of the claim providing a , which must subsequently be submitted to the relevant governmental authority to formally eliminate the claim from public records. In certain situations, for a or seek . Recent case studies emphasize the significance of comprehending the intricacies and regulations involved in the removal process. For instance, innovative funding methods, such as utilizing tax exemptions available to public facility corporations (PFCs), have become essential in navigating the challenging real estate landscape. Moreover, important Texas cases have highlighted the changing legal ideas in home financing, making it crucial for property owners to stay updated and seek professional advice when handling claims.
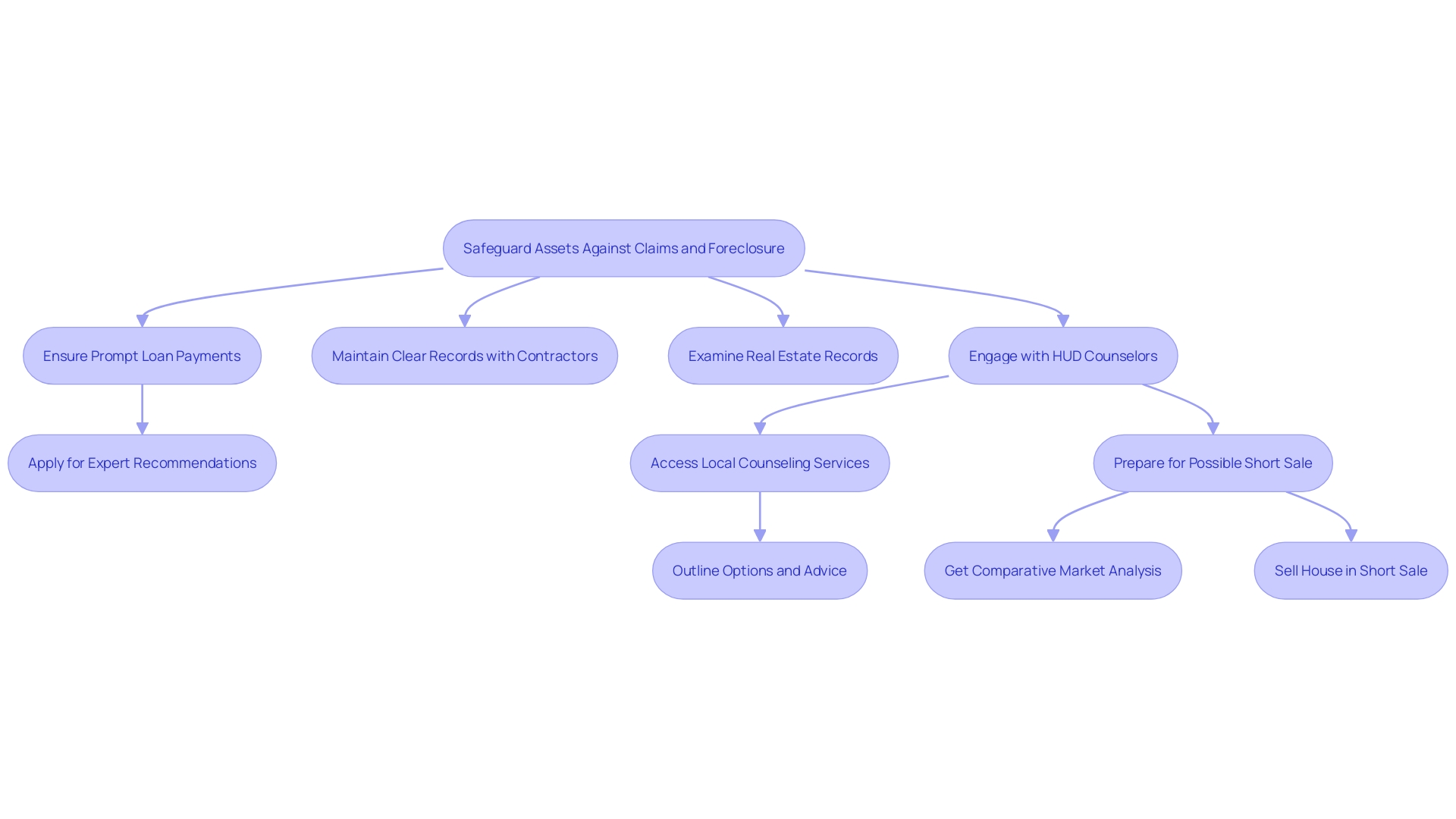
Preventing Liens: Best Practices for Homeowners
To protect against claims on their assets, homeowners must guarantee prompt payments on loans and taxes. According to recent reports, Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac have successfully completed over 43,000 foreclosure prevention actions in just the third quarter of 2023, highlighting the importance of staying current on . Furthermore, the increase in , as evidenced by the out-of-state owners of a million-dollar vacant lot in Concord who found out their land had been sold without their awareness, emphasizes the necessity for vigilance.
Homeowners should meticulously maintain clear records of any agreements with contractors and confirm that all work is completed and paid for before finalizing contracts. This practice not only prevents potential but also ensures transparency and accountability. Consistently examining real estate records can keep homeowners updated about any possible claims against their assets, assisting in preventing unwelcome surprises and legal issues.
Furthermore, engaging with housing counselors from the can provide valuable advice and resources to prevent foreclosure. HUD counselors offer free services that can outline various options and next steps to ensure homeowners stay ahead of potential financial pitfalls. With the volatile housing market, being proactive and informed is essential to maintaining and financial health.
Conclusion
Understanding the complexities of property liens is essential for anyone engaged in real estate transactions. A lien serves as a legal claim by a lender or creditor, which can significantly influence property ownership, sales, and financial obligations. Various types of liens, including mortgage, tax, judgment, and mechanic’s liens, each carry unique implications that must be carefully navigated to ensure successful transactions.
The impact of these liens on selling a house can be profound, often requiring resolution before a property can change hands, thereby complicating the selling process and potentially leading to financial losses.
Removing a lien typically necessitates settling the associated debt, followed by the issuance of a release of lien. This process can sometimes involve negotiation or legal assistance, emphasizing the need for homeowners to remain informed about the intricacies of lien removal. Preventative measures are equally important; homeowners can safeguard their properties by maintaining timely payments and keeping thorough records of financial agreements.
Engaging with housing counselors and regularly reviewing property records can further mitigate risks associated with liens.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of property liens is crucial for protecting financial interests and facilitating smoother real estate transactions. By being proactive and informed, individuals can navigate the complexities of liens, ensuring that their real estate dealings are conducted without unnecessary complications or financial repercussions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a lien?
A lien is a legal claim imposed by a lender or creditor on an asset to secure a debt or obligation. If the borrower defaults, the lienholder has the right to take possession of the asset.
How do liens affect equity in a property?
Equity is determined by comparing the estimated current value of an asset to its outstanding mortgage debt (MDO). If the MDO exceeds the property’s estimated value, it results in negative equity; if the estimated value is higher than the MDO, there is positive equity.
What types of liens exist?
Liens can be categorized into several types: Mortgage Liens (created when a borrower takes out a mortgage to buy a home), Tax Claims (imposed by government entities for unpaid real estate taxes), Judgment Claims (arising from court rulings against the asset owner), and Mechanic’s Claims (filed by contractors for unpaid work).
How do liens impact the sale of a property?
Liens must be resolved before a property can be sold. Sellers often need to clear any outstanding debts associated with the lien during closing, which can complicate their financial situation and deter potential buyers.
What happens if a property has an unresolved lien?
An unresolved lien can lead to a drop in property value, prolonged time on the market, and can make the property less appealing to buyers. Brokers are required to disclose such claims, which can significantly influence buyer decisions.
How can a lien be cleared?
Clearing a lien usually involves settling the debt that led to its establishment. Once settled, the lienholder issues a release document, which must be filed with the relevant governmental authority to remove the claim from public records.
What should homeowners do to protect against liens?
Homeowners should make timely payments on loans and taxes, maintain clear records of contracts and completed work, and regularly check real estate records for any potential claims against their property. Engaging with housing counselors can also provide valuable resources to prevent foreclosure.
Why is it important to understand liens in real estate?
Understanding liens is crucial for both buyers and sellers as they can significantly affect ownership rights, property value, and the overall transaction process. Awareness of different types of liens and their implications helps in navigating real estate deals effectively.




